Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP1-receptor co-agonist preserves cardiac function and improves survival in angiotensin II-induced heart failure model in mice: comparison to liraglutide
- PMID: 40517248
- PMCID: PMC12166642
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-025-02806-5
Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP1-receptor co-agonist preserves cardiac function and improves survival in angiotensin II-induced heart failure model in mice: comparison to liraglutide
Abstract
Background: Incretin analogues, used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity, such as GLP1-receptor agonist liraglutide (Lira) have been shown to reduce major adverse cardiac events in recent clinical trials of heart failure. Tirzepatide (TZP), a dual GIP/GLP1-receptor agonist has shown promising results in the SUMMIT trial as improved cardiovascular outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). However, data regarding their use in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is lacking. We performed a head-to-head comparative study in a mouse model of non-ischaemic cardiac injury induced by continuous angiotensin II (AngII) infusion, as AngII is a key driver of both heart failure forms.
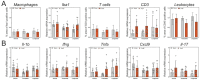
Methods: Osmotic minipumps were inserted for subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of AngII (1.5 mg/kg/day) in 5-month-old male Balb/c mice or sham surgery was performed. Animals were treated with vehicle (Veh), Lira (300 µg/day i.p.) or TZP (48 µg/day s.c.) for 14 days in the following groups: Sham/Veh (n = 7), AngII/Veh (n = 15), Sham/Lira (n = 7), AngII/Lira (n = 15), Sham/TZP (n = 8), AngII/TZP (n = 15). Cardiac structural, functional and molecular characteristics were assessed by echocardiography, ECG, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and qRT-PCR.
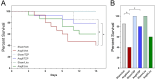
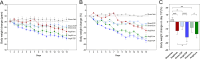
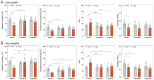
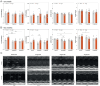
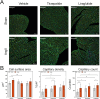
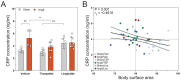
Results: Mortality was significantly higher in AngII/Veh animals compared to controls, while AngII/TZP mice showed significantly reduced mortality after 14 days of treatment. Both Lira and TZP caused significant weight reduction compared to controls. AngII given alone also reduced body mass, and this reduction was further enhanced by TZP. Treatment with both compounds preserved cardiac systolic and diastolic function compared with AngII/Veh animals, as shown by normal ejection fraction and E/e', respectively. Both Lira and TZP decreased the AngII-induced elevation of cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy markers, including Ctgf, Col1a1, Col3a1, and Nppa, while TZP also reduced the elevated Nppb level. TZP also reduced systemic inflammation, as shown by the reduction in serum CRP levels.
Conclusions: Lira and TZP preserved cardiac function and decreased markers of hypertrophy and fibrosis in mice with AngII-induced heart failure, whereas TZP also significantly decreased mortality. In addition to HFpEF, the use of incretin analogues may also be of clinical relevance in the treatment of HFrEF. However, as patients with heart failure, AngII level is elevated and can cause weight loss/cachexia, the usage of incretin analogues to treat non-obese heart failure patients should be considered.
Keywords: HFrEF; Heart failure; Incretin analogues; Liraglutide; Tirzepatide.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: P.F. is the founder and CEO of Pharmahungary Group, a group of R&D services. There is no conflict of interests on behalf any other author.
Figures

References
-
- Ryan DH, Lingvay I, Colhoun HM, Deanfield J, Emerson SS, Kahn SE, et al. Semaglutide effects on cardiovascular outcomes in people with overweight or obesity (SELECT) rationale and design. Am Heart J. 2020;229:61–9. - PubMed
-
- Marx N, Federici M, Schütt K, Müller-Wieland D, Ajjan RA, Antunes MJ, et al. 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(39):4043–140. - PubMed
-
- Vaduganathan M. GLP-1 receptor agonists in heart failure. Lancet. 2024;404(10454):727–9. - PubMed
-
- Kosiborod MN, Petrie MC, Borlaug BA, Butler J, Davies MJ, Hovingh GK, et al. Semaglutide in patients with obesity-related heart failure and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(15):1394–407. - PubMed
-
- Kosiborod MN, Abildstrøm SZ, Borlaug BA, Butler J, Rasmussen S, Davies M, et al. Semaglutide in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and obesity. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(12):1069–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

