Genetic characterization and pathogenicity analysis of three porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains isolated from North China
- PMID: 40517255
- PMCID: PMC12166606
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-025-01554-4
Genetic characterization and pathogenicity analysis of three porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains isolated from North China
Abstract
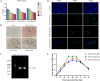
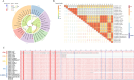
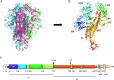
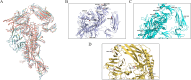
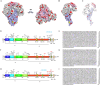
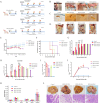
Porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED) is a highly contagious intestinal disease owing to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) infection. It is extremely detrimental to newborn piglets and has caused huge economic losses to the global pig industry. In this study, three PEDV strains of G2a PEDV-WF/2023, G2b PEDV-SX/2024 and PEDV-HS/2024 were successfully isolated from small intestine tissue samples with the analysis of their molecular structure characteristics, genetic characteristics and pathogenicity. Notably, these three PEDV strains had multiple unique aa mutations and extensive N-glycosylation in the D0 region, S1-NTD, COE epitope and SS6, respectively. Therefore, their structures were different compared to CV777 and PT-P5 strains. Furthermore, all the three PEDV strains caused severe clinical symptoms in 1-day-old piglets after infection. Among them, G2a PEDV-WF/2023 was the most detrimental to piglets, with highly levels of viral RNA in vivo. In contrast, PEDV-HS/2024 showed relatively weak pathogenicity to piglets, but it also caused the death of piglets. It might be attributed to the occurrence of individual mutations consistent with the amino acid sequence of G1b subtype in PEDV-HS/2024 strain. Findings in this study allow us to confirm that the G2a PEDV-WF/2023 strain is currently one of the most harmful epidemic strains to piglets. This study may benefit our understanding of the molecular structure characteristics, evolution trend and transmission dynamics of the epidemic strains in China. Moreover, it may provide potential reference for formulating more targeted PEDV vaccines, preventing and controlling this infection, and further curbing the cross-species spread of PEDV.
Keywords: PEDV; S protein; evolution trend; molecular structure characterization; pathogenic analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Ethics Committee at Hebei Agricultural University granted permission for the animal study, identified by the approval number 2021069. The research adhered to both institutional guidelines and local regulations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

