Smoking and bladder cancer: insights into pathogenesis and public health implications from a bibliometric analysis (1999-2023)
- PMID: 40517257
- PMCID: PMC12167575
- DOI: 10.1186/s13011-025-00658-6
Smoking and bladder cancer: insights into pathogenesis and public health implications from a bibliometric analysis (1999-2023)
Abstract
Background: Cigarette smoking is a major contributor to the global burden of bladder cancer. Its carcinogenic effects result from the harmful substances in tobacco smoke, which induce genetic mutations and disrupt cellular processes. Understanding how smoking contributes to bladder cancer is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Objective: This study systematically reviews global research on the relationship between smoking and bladder cancer through bibliometric analysis, identifying research hotspots, trends and future directions.
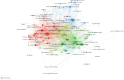
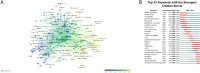
Methods: Relevant literature on the relationship between cigarette smoking and bladder cancer published between 1999 and 2023 was retrieved from the Web of Science database. Visual analyses were conducted using VOSviewer and CiteSpace software, focusing on contributions from countries, institutions, journals, authors and keywords.
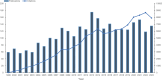
Results: Our analysis of 2,802 publications revealed an upward trend in annual output on the relationship between smoking and bladder cancer, with the United States and China as leading contributors. Notable institutions included the NIH, National Cancer Institute, University of Texas System and the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Key journals were Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention and International Journal of Cancer. Rothman, Nathaniel and Zeegers, M.P.A. were the most productive and co-cited authors. Keyword analysis highlighted DNA repair, genome-wide association studies, and smoking cessation.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis has significantly advanced the field by highlighting current research directions and the application of specific mechanisms. These findings also have implications for clinical practice and public health policy, potentially improving patient outcomes through a comprehensive understanding of disease pathogenesis.
Keywords: Bibliometrics; Bladder cancer; Citation analysis; International collaboration; Smoking.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study did not involve any experiments on humans or animals, and thus, ethical approval was not required. Consent for publications: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
-
Global research trends and hotspots on imaging of bladder cancer: A bibliometric and visual analysis from 1981 to 2023.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Mar 21;104(12):e41907. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041907. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40128048 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric insight into neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bladder cancer: trends, collaborations, and future avenues.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 19;15:1297542. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1297542. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38444854 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric and visual analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 19;14:1323115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323115. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38173726 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Hoogstraten LMC, Vrieling A, van der Heijden AG, Kogevinas M, Richters A, Kiemeney LA. Global trends in the epidemiology of bladder cancer: challenges for public health and clinical practice. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20(5):287–304. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Leal J, Luengo-Fernandez R, Sullivan R, Witjes JA. Economic Burden of Bladder Cancer Across the European Union. Eur Urol. 2016;69(3):438–47. - PubMed
-
- Burger M, Catto JW, Dalbagni G, Grossman HB, Herr H, Karakiewicz P, Kassouf W, Kiemeney LA, La Vecchia C, Shariat S, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2013;63(2):234–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

