Modulation of motor excitability reflects traveling waves of neural oscillations
- PMID: 40517384
- PMCID: PMC12257788
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115864
Modulation of motor excitability reflects traveling waves of neural oscillations
Abstract
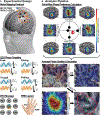
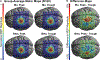
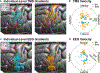
Neural traveling waves represent an important endogenous phenomenon with structural and functional relevance in the human brain. These waves, commonly recorded via electroencephalogram (EEG) or electrocorticography (ECoG), are implicated in a range of brain processes. However, it remains unclear how they influence neural excitability across brain regions. Advancements in real-time control of brain stimulation present opportunities to compare traveling waves and excitation. Here, we investigate how sensorimotor mu (8-13 Hz) and beta (14-30 Hz) traveling waves affect motor cortex excitability using real-time EEG-controlled transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). We observed gradients in the mediolateral direction and then validated these findings using ECoG recordings in a human participant and a nonhuman primate. Our results demonstrate that neuronal excitability reflects the natural patterns of sensorimotor traveling waves. This provides important evidence of traveling waves modulating neural excitability in humans. This opens possibilities for more effective stimulation protocols aligned with intrinsic brain dynamics.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; TMS-EEG; closed-loop; electrocorticography; electroencephalography; motor cortex; real-time stimulation; transcranial magnetic stimulation; traveling waves.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.O., I.A., and S.S. are inventors on patent applications describing TMS closed-loop stimulation technology.
Figures

References
-
- Ermentrout GB, and Kleinfeld D (2001). Viewpoint Traveling Electrical Waves in Cortex: Insights from Phase Dynamics and Speculation on a Computational Role the Results The Amplitude of the Wave Is a Periodic Function of Time. Soc. Neurosci. 29, 33–44. - PubMed
-
- Hughes JR (1995). The Phenomenon of Travelling Waves: A Review. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 26, 1–6. - PubMed
-
- Hindriks R, van Putten MJAM, and Deco G (2014). Intra-cortical propagation of EEG alpha oscillations. Neuroimage 103, 444–453. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

