Clonal Hematopoiesis: Impact on Health and Disease
- PMID: 40517440
- PMCID: PMC12167641
- DOI: 10.1002/hon.70075
Clonal Hematopoiesis: Impact on Health and Disease
Abstract
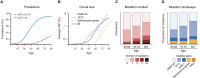
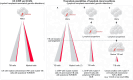
The expansion of hematopoietic cell clones, carrying alterations in genes frequently mutated in hematologic malignancies, in the absence of altered hematopoietic cell counts or otherwise defined disease criteria, is termed clonal hematopoiesis (CH). CH is frequently detectable in aged individuals and associates with numerous detrimental health impacts. These impacts are highly dependent on the type of mutations and the cellular context in which they manifest. Mutations in the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) compartment as well as in self-renewing more mature cells associate with increased risks of malignant disease, while mutations penetrating via hematopoiesis in non-self-renewing, mature cells associate with altered immune functions and consequent systemic effects, which can initiate or aggravate multiple non-malignant diseases. Here we review the definitions of CH, major genetic drivers and lineage penetrance, and we highlight how CH impacts on hematological and non-hematological conditions.
Keywords: clonal hematopoiesis; health outcomes; leukemia.
© 2025 The Author(s). Hematological Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

