Multiomics identifies tumor-intrinsic SREBP1 driving immune exclusion in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40518290
- PMCID: PMC12314812
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2025-011537
Multiomics identifies tumor-intrinsic SREBP1 driving immune exclusion in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
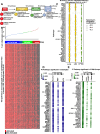
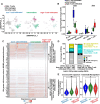
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have improved patient outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); however, most patients do not experience durable benefit. The non-T cell-inflamed tumor microenvironment, characterized by limited CD8+ T-cell infiltration, reduced dendritic cell function, and low interferon-γ-associated gene expression, is associated with a lower likelihood of response to ICI. To nominate new therapeutic targets for overcoming ICI resistance in HCC, we conducted a large-scale multiomic analysis on 900+human specimens (RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), proteomics) and 31 tumor single-cell (sc) RNA-seq samples, with tissue validation through imaging mass cytometry (IMC) and spatial lipidomics by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI), with experimental investigation by in vitro CD8+ T-cell recruitment and macrophage polarization functional assays using three-dimensional (3D) co-culture models. We discovered 32 oncogenic pathways associated with immune exclusion, with sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 (SREBP1, encoded by SREBF1) as a hub regulator. scRNA-seq analysis showed that SREBP1 signaling is associated with enriched lipid biogenesis pathways in tumor cells, elevated immunosuppressive markers in macrophages, and diminished CD8+ T-cell infiltration. Integration of IMC and MALDI images revealed distinct lipid species differentially abundant in tumor regions with low versus high CD8+ T cell infiltration. Functional studies in a 3D in vitro tumor-immune co-culture system demonstrated that CRISPR-mediated SREBF1 knockout (KO) in HepG2 cells reduced monocyte recruitment, decreased expression of the protumorigenic CD206 marker in macrophages, and enhanced CD8+ T-cell migration compared with wild-type (WT) (p<0.0001). RNA-seq of SREBF1 KO versus WT tumor cells confirmed suppression of lipid biosynthesis genes.Our findings nominate an atlas of tumor-intrinsic drivers of immune exclusion, particularly SREBP1 via pro-tumorigenic macrophage (M2-like) reprogramming. These pathways may represent novel therapeutic targets to enhance antitumor immunity and deserve further study as targeted therapy candidates to enhance ICI in HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Tumor microenvironment - TME.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RB declares PCT/US15/612657 (Cancer Immunotherapy), PCT/US18/36052 (Microbiome Biomarkers for Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Responsiveness: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Uses Thereof), PCT/US63/055227 (Methods and Compositions for Treating Autoimmune and Allergic Disorders). JJL declares DSMB: AbbVie, Immutep; Scientific Advisory Board: (no stock) 7 Hills, Fstar, Inzen, RefleXion, Xilio (stock) Actym, Alphamab Oncology, Arch Oncology, Kanaph, Mavu, Onc.AI, Pyxis, Tempest; Consultancy with compensation: AbbVie, Alnylam, Avillion, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Checkmate, Codiak, Crown, Day One, Eisai, EMD Serono, Flame, Genentech, Gilead, HotSpot, Kadmon, KSQ, Janssen, Ikena, Immunocore, Incyte, Macrogenics, Merck, Mersana, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Ribon, Rubius, Silicon, Synlogic, Synthekine, TRex, Werewolf, Xencor; Research Support: (all to institution for clinical trials unless noted) AbbVie, Agios (IIT), Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb (IIT & industry), Corvus, Day One, EMD Serono, Fstar, Genmab, Ikena, Immatics, Incyte, Kadmon, KAHR, Macrogenics, Merck, Moderna, Nektar, Next Cure, Numab, Pfizer (IIT & industry) Replimmune, Rubius, Scholar Rock, Synlogic, Takeda, Trishula, Tizona, Xencor; Patents: (both provisional) Serial #15/612,657 (Cancer Immunotherapy), PCT/US18/36052 (Microbiome Biomarkers for Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Responsiveness: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Uses Thereof). SPM declares research grants from Alnylam Pharmaceuticals and Fog Pharmaceuticals and is a consultant for and on Advisory Boards for Surrozen, AntlerA, Alnylam, Mermaid Bio, Vicero Inc, and UbiquiTx; however, there are no pertinent conflicts of interest related to the current manuscript. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to JJL (lukejj@upmc.edu) and RB (baor@upmc.edu). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
