PARP-1 as a novel target in endocrine-resistant breast cancer
- PMID: 40518539
- PMCID: PMC12168341
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-025-03441-4
PARP-1 as a novel target in endocrine-resistant breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Several mechanisms are involved in the resistance to endocrine therapy (ET) in estrogen receptor (ERα)-positive breast cancer (BC), including acquired mutations of ERα gene (ESR1). For example, the frequent mutation, Y537S, was shown to trigger a constitutively active receptor leading to reduced affinity for both agonist and antagonist ligands. The development of more comprehensive therapies remains a challenge in BC patients exhibiting activating mutations in ERα. Here, we show that Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) may be considered as a novel therapeutic target in ERα-positive BC.
Methods: ERα wild type or Y537S mutated MCF7 and T47D BC cell lines were used as model systems. Immunoblotting, immunofluorescence, gene silencing, real-time PCR, promoter assays, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) as well as cell viability, colony and cell cycle assays served to investigate the involvement of PARP-1 in BC progression. The growth of MCF7 ERα Y537S cells injected into the mammary ducts of NSG mice and treated with the ERα antagonist lasofoxifene or the PARP-1 inhibitor niraparib was monitored by luminescence imaging, weight measurement, and histological analysis. RNA sequencing studies were performed on the above-described xenograft tumors. METABRIC dataset was used to evaluate the clinical significance of PARP-1 and the biological role of the PARP-1-associated genes in ERα-positive BC patients.
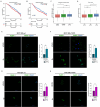
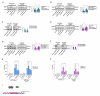
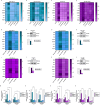
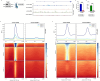
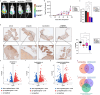
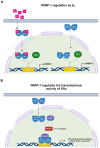
Results: We first demonstrated that the up-regulation of PARP-1 expression induced by estrogens is abrogated either by inhibiting or silencing ERα in MCF7 and T47D BC cells expressing ERα wild type or Y537S mutation. We then showed that PARP-1 is involved in the binding of ERα and its co-activator FoxA1 to the promoters of several target genes, as determined by ChIP-sequencing studies. Of note, the inhibition of PARP-1 prevented the proliferative effects mediated by ERα in BC cells expressing either wild type or Y537S ERα. In accordance with these findings, the growth of xenograft tumors derived from MCF7 ERα Y537S BC cells was significantly reduced using niraparib and lasofoxifene. Finally, RNA-sequencing analyses showed that ERα signaling is downregulated by niraparib compared to vehicle-treated tumors.
Conclusions: Overall, our results suggest that PARP-1 should be explored as a potential target in comprehensive therapeutic approaches in ET-resistant BC.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Endocrine therapy; Niraparib; PARP-1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures conformed to the Helsinki Declaration for the research on humans. Consent for publication: All the authors agree to publish this paper. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting tumour re-wiring by triple blockade of mTORC1, epidermal growth factor, and oestrogen receptor signalling pathways in endocrine-resistant breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 8;20(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-0983-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29880014 Free PMC article.
-
Timeless Is a Novel Estrogen Receptor Co-activator Involved in Multiple Signaling Pathways in MCF-7 Cells.J Mol Biol. 2018 May 11;430(10):1531-1543. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.03.008. Epub 2018 Mar 16. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29555554
-
Novel inhibitors of PARP1 and PARP14: design, synthesis, and potentiation of cisplatin efficacy in cancer.Future Med Chem. 2025 Jan;17(1):35-58. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2437972. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39691063
-
Olaparib Monotherapy or in Combination with Abiraterone for the Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC) and a BRCA Mutation.Target Oncol. 2025 May;20(3):445-466. doi: 10.1007/s11523-025-01146-4. Epub 2025 May 21. Target Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40397306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Mechanisms of Actions, Effects, and Clinical Implications of PARP Inhibitors in Epithelial Ovarian Cancers: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 23;23(15):8125. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158125. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897700 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

