Nephroprotective Effects of Fraxinus Hookeri Wenz. Against Renal Toxicity and DNA Oxidative Damages Induced by CCl4 in Rats
- PMID: 40518992
- PMCID: PMC12368880
- DOI: 10.1002/open.202400515
Nephroprotective Effects of Fraxinus Hookeri Wenz. Against Renal Toxicity and DNA Oxidative Damages Induced by CCl4 in Rats
Abstract
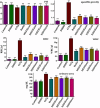
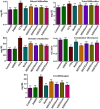
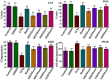
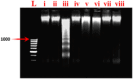
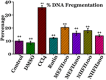
Recognizing the therapeutic value of the Genus Fraxinus worldwide, this study evaluates the antioxidant potential of Fraxinus hookeri Wenz. (F. hookeri) against CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Forty-eight rats are randomly allocated into eight groups (six rats each). Antioxidant enzymes, genotoxicity, urine and serum markers, and tissue histopathology are assessed to determine their nephroprotective effects. The Control group remains untreated, while the DMSO group receives vehicle olive oil intraperitoneally and DMSO orally (3 ml/kg). All other groups, except Control and DMSO, are given CCl4 (3 ml/kg, i.p., in 30% olive oil) twice weekly for 4 weeks. The CCl4 group receives only CCl4. The Rutin group receives reference drug Rutin orally (50 mg/kg). MEFH100 and MEFH200 groups are given MEFH at 100 and 200 mg/kg, respectively, and NHFH100 and NHFH200 receive NHFH at the same doses. Rutin and F. hookeri treatment effectively (P < 0.05) restore urine and serum markers disrupted by CCl4. CCl4 reduced (p < 0.05) antioxidant enzymes (CAT, SOD, POD) and increased TBAR levels and DNA damage, which are reversed by cotreatment with F. hookeri and Rutin. Histopathological improvements (P < 0.05) are also observed with F. hookeri. The results indicate that F. hookeri enhances antioxidant defenses, supporting its potential against CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity.
Keywords: Fraxinus hookeri; CCl4; genotoxicity; histopathology; nephroprotective; nephrotoxicity; renal.
© 2025 The Author(s). ChemistryOpen published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyzes, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

