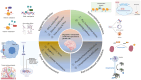
Regulatory mechanisms of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase expression in glioma cells
- PMID: 40519114
- PMCID: PMC12174773
- DOI: 10.1177/00368504251345014
Regulatory mechanisms of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase expression in glioma cells
Abstract
O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT), a pivotal DNA repair enzyme, has its dysregulation playing a substantial role in gliomagenesis, the development of therapeutic resistance, and patient prognosis. This narrative review is designed to offer an all-encompassing overview of the intricate regulatory mechanisms that govern MGMT expression in glioma cells. We systematically investigate the diverse levels of regulation that impact MGMT expression in glioma. These include epigenetic regulation, transcriptional control, post-translational modifications, and the influence exerted by the tumor microenvironment. Epigenetically, methylation of CpG islands within the MGMT promoter region represents a critical determinant for gene silencing. Conversely, histone modifications such as H3K4me3 augment MGMT expression. Transcriptionally, a complex network of transcription factors, which encompasses Sp1, p53, and NF-κB, along with signaling pathways like TGF-β, JAK/STAT, and PI3K/AKT, orchestrates MGMT expression in glioma cells. Furthermore, post-translational modifications of MGMT, such as phosphorylation and ubiquitination, are of pivotal importance in modulating its stability and enzymatic activity. The tumor microenvironment, with factors such as oxidative stress, hypoxia, and immune responses, also exerts a significant influence on MGMT expression. This narrative review delves deeper into the relationship between MGMT expression and drug resistance, especially resistance to alkylating chemotherapy agents, and accentuates the significance of evaluating MGMT expression for personalized glioma therapy. By elucidating these regulatory mechanisms, this review endeavors to enhance our understanding of MGMT's role in glioma biology and to provide insights for future therapeutic strategies aimed at surmounting current treatment challenges.
Keywords: Drug resistance; O6-methylguanine methyltransferase; glioma; regulatory mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MGMT testing for glioma in clinical laboratories: discordance with methylation analyses prevents the implementation of routine immunohistochemistry.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Nov;138(11):1789-97. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1312-1. Epub 2012 Sep 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22986811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic and predictive value of epigenetic silencing of MGMT in patients with high grade gliomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurooncol. 2011 Nov;105(2):325-35. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0594-5. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Neurooncol. 2011. PMID: 21523485
-
AI-driven estimation of O6 methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation in glioblastoma patients: a systematic review with bias analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jan 31;150(2):57. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05566-5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38291266 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and epigenetic alterations in MGMT gene and correlation with concomitant chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in cervical cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(16):15159-15170. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05305-w. Epub 2023 Aug 27. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37634205 Free PMC article.
-
MGMT methylation and its prognostic significance in inoperable IDH-wildtype glioblastoma: the MGMT-GBM study.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024 Oct 5;166(1):394. doi: 10.1007/s00701-024-06300-x. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024. PMID: 39367282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awwad SW, Serrano-Benitez A, Thomas JC, et al. Revolutionizing DNA repair research and cancer therapy with CRISPR-Cas screens. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2023; 24: 477–494. - PubMed
-
- Mohile NA, Messersmith H, Gatson NT, et al. Therapy for diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors in adults: ASCO-SNO guideline. J Clin Oncol 2022; 40: 403–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous