Interferon-Stimulated Genes: Novel Targets in Renal Pathogenesis
- PMID: 40519215
- PMCID: PMC12165645
- DOI: 10.1159/000546141
Interferon-Stimulated Genes: Novel Targets in Renal Pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: Kidney diseases are a prevalent global health concern, and despite ongoing research, there remains a lack of fully effective clinical treatments to prevent or halt their progression. Consequently, it is encouraged to identify novel biomarkers, establish early diagnostic methods, pinpoint key molecular pathways, and develop innovative therapeutic targets for more effective management of renal disorders.
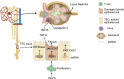
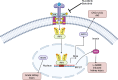
Summary: Interferons (IFNs), a group of cytokines, play pivotal roles in immune responses, particularly in antiviral and antiproliferative activities. IFNs trigger a cascade of signaling events that lead to the induction of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), which are essential for controlling viral infections and regulating immune responses. This review explores the impact of interferon-related genes on renal disorders, focusing on the mechanisms, therapeutic approaches, and consequences of enhanced interferon signaling in the kidney.
Key messages: Most diagnostic and therapeutic strategies targeting ISGs are still far from clinical implementation. The better understanding of ISG-regulated pathophysiology and the progress of new intervention approaches are expected to facilitate the clinical translation of ISGs-based diagnosis and therapy of kidney diseases.
Keywords: Immune regulation; Interferon signaling; Interferon-stimulated genes; Renal pathogenesis; Therapeutic target.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of Interferon-Stimulated Gene Induction in HIV-1-Infected Macrophages.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e00744-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00744-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28768867 Free PMC article.
-
Interference without interferon: interferon-independent induction of interferon-stimulated genes and its role in cellular innate immunity.mBio. 2024 Oct 16;15(10):e0258224. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02582-24. Epub 2024 Sep 20. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39302126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UL26 Attenuates IKKβ-Mediated Induction of Interferon-Stimulated Gene (ISG) Expression and Enhanced Protein ISGylation during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection.J Virol. 2019 Nov 13;93(23):e01052-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01052-19. Print 2019 Dec 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31534044 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-Stimulated Genes: What Do They All Do?Annu Rev Virol. 2019 Sep 29;6(1):567-584. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015756. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Annu Rev Virol. 2019. PMID: 31283436 Review.
-
The Growth Factors: Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Kidney Diseases.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022 Sep 12;8(5):368-380. doi: 10.1159/000526208. eCollection 2022 Nov. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36466071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Francis A, Harhay MN, Ong ACM, Tummalapalli SL, Ortiz A, Fogo AB, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: an international consensus. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024;20(7):473–85. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

