Global T-cell functionality evaluated by whole blood interferon-gamma release assay as a valuable indicator for immune reconstitution monitoring in pediatric allo-HSCT
- PMID: 40519737
- PMCID: PMC12163798
- DOI: 10.21037/tp-2025-80
Global T-cell functionality evaluated by whole blood interferon-gamma release assay as a valuable indicator for immune reconstitution monitoring in pediatric allo-HSCT
Abstract
Background: Adequate T-cell immune reconstitution (IR) following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is pivotal for the recovery and optimal outcomes of pediatric HSCT recipients. A thorough assessment of global T-cell functionality is a crucial component in monitoring T-cell IR during the post-transplant period. The purpose of this study is to provide a novel tool and strategy for assessing and monitoring T-cell IR after pediatric allo-HSCT.
Methods: This study enrolled 126 pediatric patients receiving allo-HSCT at a single institution. A standardized whole blood interferon-gamma release assay (WB-IGRA) was introduced to evaluate global T-cell functionality in different periods after HSCT.
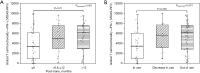
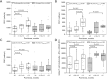
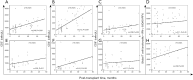
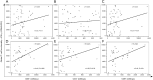
Results: The study revealed that T-cell functionality, assessed via the WB-IGRA assay, progressively enhanced over the post-transplant period, effectively distinguishing between patients with and without immunosuppression, thereby highlighting the assay's viability in assessment of T-cell IR in children after allo-HSCT. Further analysis stratified by age revealed a more significant enhancement in T-cell functionality among children >10 years old compared to those ≤10. Conversely, when evaluating immune cell subsets, increases in CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ subsets well reflected immune reconstructive progress in children ≤10 years old, whereas only increases in CD4+ cell subsets exhibited statistical significance in older children. Additionally, all three T cell subset counts were significantly correlated with T-cell functionality in older children, whereas no such correlation was observed in younger ones.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated the potential application of the WB-IGRA approach in evaluating and monitoring T-cell IR in pediatric allo-HSCT recipients. Combining the assessment of T-cell immune functionality with cellular phenotypes could enhance the understanding of T-cell IR in HSCT children of different ages.
Keywords: Pediatric patients; T-cell functionality; allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT); immune reconstitution (IR).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tp.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tp-2025-80/coif). L.M., A.F., F.B. and J.L. are bioMérieux employees. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon gamma release assay has potential in the prediction of chronic graft-versus-host disease in recipients of myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide-based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis.Transpl Immunol. 2025 Feb;88:102166. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2024.102166. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Transpl Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39716645
-
Humoral Immune Reconstitution Kinetics after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children: A Maturation Block of IgM Memory B Cells May Lead to Impaired Antibody Immune Reconstitution.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017 Sep;23(9):1437-1446. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 8. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28495643
-
Temporal Evolution of Functional Immune Reconstitution after Allogeneic HSCT.Transplant Cell Ther. 2025 Jun;31(6):367-381. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2025.03.001. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Transplant Cell Ther. 2025. PMID: 40058647
-
Immune Reconstitution after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Children.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016 Feb;22(2):195-206. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.08.028. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26341398 Review.
-
Optimizing the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection in allo-HSCT recipients.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023 Feb;19(2):227-235. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2023.2161510. Epub 2023 Jan 1. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36541485 Review.
References
-
- Talekar MK, Olson T. Immune Reconstitution After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. In: Brown V. editor. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Pediatric Hematologist/Oncologist. Cham: Springer, 2008:371-83.
-
- Beksac M. editor. Bone marrow and stem cell transplantation (Vol. 134). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2007.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
