Serum IL-6 predicts immunotherapy-related adverse and outcome in advanced gastric and esophageal cancer patients with Anti-PD-1 treatment
- PMID: 40519900
- PMCID: PMC12163003
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1553882
Serum IL-6 predicts immunotherapy-related adverse and outcome in advanced gastric and esophageal cancer patients with Anti-PD-1 treatment
Abstract
Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) significantly prolong the survival of cancer patients. including gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC) and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients. Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are inevitably involved in ICIs treatment sometimes with severe consequences. Extreme caution is necessary for predicting irAEs and precisely screening of appropriate patients. We evaluated the association of interleukin-6 (IL-6) with irAEs and their impacts on ICIs treatment effectiveness in advanced GAC and ESCC patients.
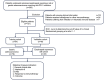
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 121 patients treated with ICIs between March 1, 2020 and August 31, 2023 to evaluate the association between serum IL-6 and ICIs treatment effectiveness. The occurrence of irAEs, including grade and category, and effectiveness of immunotherapy, including objective remission rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), was evaluated. Categorical count data were tested by chi-square test. Nonparametric rank sum tests were performed using Wilcoxon and Kruskal-Wallis test. Survival rate estimation and survival curves were generated using Kaplan-Meier curve and Log-rank test. Univariate and multivariable COX regression analyses were performed to identify independent prognostic factors.
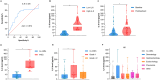
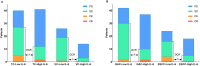
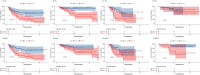
Results: A total of 121 patients including 79 with GAC and 42 with ESCC patients were randomly divided into TC (n=81) and VC (n=40) groups. Higher serum IL-6 levels were associated with increased incidence of irAEs, the outcome analysis also indicated its association with lower DCR, shorter PFS and shorter OS in TC group. The higher IL-6 related irAEs occurrence and poor prognosis (DCR, PFS) was confirmed in the VC group. Individual tumor analysis showed that higher IL-6 was associated with both irAEs occurrence and poor prognosis (DCR, PFS, OS) in ESCC patients, and with irAEs occurrence and poor prognosis (DCR, PFS) in GAC patients. No statistically significant associations were observed between pathological biomarkers including programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), mismatch repair (MMR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and either IL-6 levels or irAEs occurrence in both GC and ESCC patients.
Conclusion: Elevated serum IL-6 levels were associated with the incidence of irAEs, and higher IL-6 levels predicted worse prognosis in GAC and ESCC patients with ICIs treatment.
Keywords: esophageal cancer; gastric cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immune-related adverse events; interleukin-6; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Zhang, Jiao, Ding, Wang, Zhao, Wu and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the treatment efficacy and prognostic factors of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a multicenter, retrospective clinical study.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 24;15:1468342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1468342. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39512347 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 is a prognostic biomarker in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma received with PD-1 inhibitors.Front Immunol. 2025 May 13;16:1569042. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1569042. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40433391 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of immunotherapy in real-world patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2025;43:100908. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2025.100908. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40187204
-
Efficacy and safety of PD-1 inhibitors as second-line treatment for advanced squamous esophageal cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis with a focus on PD-L1 expression levels.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 23;15:1510145. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1510145. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39916953 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for unresectable, locally advanced, HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1566939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1566939. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40207218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janjigian YY, Shitara K, Moehler M, Garrido M, Salman P, Shen L, et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England). (2021) 398:27–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00797-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rha SY, Oh DY, Yañez P, Bai Y, Ryu MH, Lee J, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy for HER2-negative advanced gastric cancer (KEYNOTE-859): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2023) 24:1181–95. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00515-6 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

