Research progress of B7-H3 in malignant tumors
- PMID: 40519928
- PMCID: PMC12162284
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1586759
Research progress of B7-H3 in malignant tumors
Erratum in
-
Correction: Research progress of B7-H3 in malignant tumors.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 17;16:1641733. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1641733. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40534877 Free PMC article.
Abstract
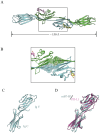
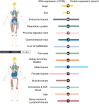
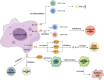
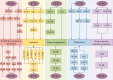
B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3, also known as CD276) is a novel member of the B7 immune protein family. There is a marked difference in the expression and distribution of B7-H3 protein and mRNA between normal and tumor tissues, with widespread expression in tumor tissues and a close relationship with tumor progression. B7-H3 activates or inhibits tumor immune responses by binding to receptors on the surface of immune cells. Apart from participating in tumor immune activities, it has regulatory effects on non-immunological functions, such as tumor migration and invasion, angiogenesis, glycometabolism, and drug resistance. Thus, it has important biological functions in regulating the progression of malignant tumors. Current research on the structure, function, and therapeutic methods of B7-H3 is continuously breaking new ground, deepening our understanding of B7-H3, and promoting the development of therapeutic drugs targeting this new protein. This review briefly discusses the structure and distribution of B7-H3, as well as its immune and non-immune functions in the progression of cancer. It also summarizes the research progress on drugs targeting B7-H3 and the latest developments in clinical trials, highlighting their significant potential for the treatment of malignant tumors.
Keywords: B7-H3(CD276); drug trials; immunity; malignant tumor; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Zhang and Shang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

