Photoacoustic imaging detects cerebrovascular pathological changes in sepsis
- PMID: 40519982
- PMCID: PMC12166994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2025.100737
Photoacoustic imaging detects cerebrovascular pathological changes in sepsis
Abstract
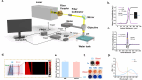
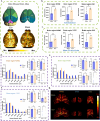
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is a common complication of sepsis, involving acute brain dysfunction. Although cerebrovascular impairment plays a critical role in SAE, sepsis-induced microvascular changes remain poorly quantified. Here, we used photoacoustic microscopy to dynamically assess blood-brain barrier permeability in septic mice, analyzing vascular structure across five parameters. Additionally, we examined pathological changes in major cortical regions and conducted behavioral tests to validate the findings. Results showed microvascular degeneration, including reduced vascular density and branching, alongside an increase in fine vessels. Motor-related cortical areas were most affected, correlating with severe motor and cognitive deficits in septic mice. This study provides the first in vivo, multi-parametric analysis of sepsis-induced cerebrovascular pathology, revealing region-specific damage. Our findings directly link microvascular dysfunction to SAE progression and highlight photoacoustic microscopy's potential in neuroscience research.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier permeability; Cerebrovascular morphology; Cortical brain regions; Photoacoustic microscopy; Sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic encephalopathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 27;17(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1689-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 31987040 Free PMC article.
-
Photoacoustic microscopy of obesity-induced cerebrovascular alterations.Neuroimage. 2019 Mar;188:369-379. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.12.027. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30553918 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic neurotransmission mediated cognitive dysfunction in two mouse models of sepsis-associated encephalopathy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):e14655. doi: 10.1111/cns.14655. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38433019 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy and septic encephalitis: an update.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021 Feb;19(2):215-231. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1812384. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021. PMID: 32808580 Review.
-
Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction.Inflammation. 2021 Dec;44(6):2143-2150. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01501-3. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 34291398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Widmann C.N., Heneka M.T. Long-term cerebral consequences of sepsis [J] Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(6):630–636. - PubMed
-
- Sonneville R., de Montmollin E., Poujade J., et al. Potentially modifiable factors contributing to sepsis-associated encephalopathy [J] Intensive care Med. 2017;43(8):1075–1084. - PubMed
-
- Gofton T.E., Young G.B. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy [J] Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012;8(10):557–566. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

