Pathogenesis and treatment strategies of sepsis-induced myocardial injury: modern and traditional medical perspectives
- PMID: 40520010
- PMCID: PMC12160516
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.111288
Pathogenesis and treatment strategies of sepsis-induced myocardial injury: modern and traditional medical perspectives
Abstract
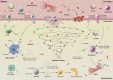
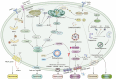
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Myocardial injury is a common complication in sepsis patients, which accelerates the progression of sepsis, leading to multiple organ dysfunction and poor prognosis. However, there are still many uncertainties about the characteristics, pathogenesis, treatment, and prognosis of sepsis-induced myocardial injury. While modern medical approaches dominate current clinical management of sepsis-induced myocardial injury, emerging evidence highlights the growing therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine in this field, driven by advances in biomedical research. The integration of these two paradigms holds promise for elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms and identifying novel therapeutic targets for sepsis-induced myocardial injury, which may accelerate the development of innovative treatment strategies. Therefore, this review comprehensively summarizes the pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions of sepsis-induced myocardial injury from both modern medicine and traditional Chinese medicine perspectives, and critically analyzes the two aiming to provide a valuable reference for researchers' understanding of sepsis-induced myocardial injury.
Keywords: Modern medicine; Myocardial injury; Pathogenesis; Sepsis; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting the immuno-inflammatory-microbial network: a key strategy for sepsis treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1575516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1575516. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40297590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Current research status and prospects of ginseng's regulatory effect on immune dysfunction caused by "acute deficiency syndrome" of sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jul;36(7):681-686. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240422-00366. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39223880 Review. Chinese.
-
Review of research progress on the role of the effective components of traditional Chinese medicine in sepsis with multiple organ dysfunction.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 28;9(11):e21713. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21713. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of the therapeutic effects of traditional Chinese medicine in sepsis-associated encephalopathy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Nov 15;334:118588. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118588. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39029543 Review.
-
Regulation of Sirtuins in Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Damage: The Underlying Mechanisms for Cardioprotection.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Feb 4;29(2):54. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2902054. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38420792 Review.
References
-
- Frencken JF, Donker DW, Spitoni C, Koster-Brouwer ME, Soliman IW, Ong DSY. et al. Myocardial Injury in Patients With Sepsis and Its Association With Long-Term Outcome. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2018;11:e004040. - PubMed
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R. et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017;45:486–552. - PubMed
-
- Nadeem R, Sockanathan S, Singh M, Hussain T, Kent P, AbuAlreesh S. Impact of Dobutamine in Patients With Septic Shock: A Meta-Regression Analysis. Am J Ther. 2017;24:e333–e46. - PubMed
-
- Cong S, Wu G, Jin Y, Zhu L. Efficacy and Adverse Reactions of Dahuang Mudan decoction Combined with Laparoscopy in the Treatment of Appendicitis: A Meta-Analysis. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023;29:822–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

