ITLN1 exacerbates Crohn's colitis by driving ZBP1-dependent PANoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells through antagonizing TRIM8-mediated CAPN2 ubiquitination
- PMID: 40520022
- PMCID: PMC12160931
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.105550
ITLN1 exacerbates Crohn's colitis by driving ZBP1-dependent PANoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells through antagonizing TRIM8-mediated CAPN2 ubiquitination
Abstract
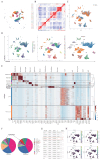
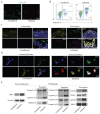
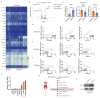
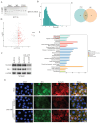
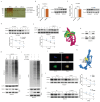
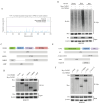
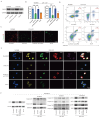
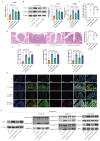
Background: This study aimed to investigate the mechanisms by which PANoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) promotes Crohn's disease (CD) progression. Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed on inflamed and uninflamed colon tissues from patients with CD. The biological functions of intelectin-1 (ITLN1) in inflammation and PANoptosis were verified through in vitro experiments. The molecular mechanisms underlying its biological functions were examined using co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) combined with mass spectrometry (MS) and RNA-seq and further validated with rescue experiments. Additionally, the in vivo function of ITLN1 regulation on inflammation, PANoptosis, and the intestinal mucosal barrier was explored in interleukin-10 knockout (IL-10 KO) colitis model mice. Results: ITLN1 was significantly overexpressed in IECs from inflamed colon tissues and specifically associated with CD-related inflammatory markers. RNA-seq and in vitro experiments indicated that ITLN1 promotes inflammation, PANoptosis, and impaired tight junctions. Co-IP and MS analyses revealed that ITLN1 can bind to the PANoptosis-promoting protein calpain-2 (CAPN2) and enhance its stability. The E3 ubiquitin ligase, a tripartite motif containing 8 (TRIM8), directly interacts with CAPN2 and mediates its ubiquitination degradation. ITLN1 can bind to TRIM8, and its impact on inflammation and Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1)-induced PANoptosis can be antagonized by CAPN2. These in vivo studies indicated that short hairpin-ITLN1 improves colonic inflammation and intestinal barrier function in IL-10 KO mice. Conclusion: We identified the ITLN1-TRIM8-CAPN2 axis that drives IEC PANoptosis in CD progression. Pharmacological inhibition of ITLN1 significantly mitigated epithelial damage and colitis both in vivo and in vitro, establishing ITLN1-targeted therapies and PANoptosis modulation as viable clinical strategies for CD treatment.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; ITLN1/TRIM8/CAPN2 axis; PANoptosis; ubiquitination.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

