Modified ZhuJing pill protects retinal pigment epithelium against oxidative stress-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Nrf2-mediated Akt/GSK3β pathway
- PMID: 40520173
- PMCID: PMC12162958
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545731
Modified ZhuJing pill protects retinal pigment epithelium against oxidative stress-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Nrf2-mediated Akt/GSK3β pathway
Abstract
Background: The modified ZhuJing pill (mZJP) has been widely used in China as a classical prescription for treating retinal diseases for years. Our preliminary experiment showed that mZJP exerted an antioxidant effect in treating dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Nevertheless, the specific mechanism underpinning the impact of mZJP on dry AMD remains obscure.
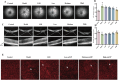
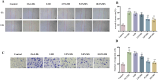
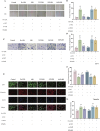
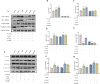
Methods: The chemical metabolites of mZJP were qualitatively analyzed using LC-Q-TOF-MS. Dry AMD model mice were used to assess the efficacy of mZJP through optical coherence tomography (OCT), fundus autofluorescence (FAF), and immunofluorescence. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in OxLDL-induced ARPE-19 cells was evaluated by monitoring cellular integrity and quantifying EMT-related markers. Cell migration capacity was determined via wound healing and transwell assays. To investigate molecular mechanisms, cells were transfected with Nrf2 siRNA and analyzed through Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and migration assays under Nrf2 inhibition.
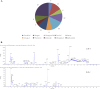
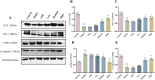
Results: A total of 113 major metabolites were identified in mZJP. Our findings revealed that mZJP alleviated retinal pathological alterations and inhibited EMT progression. Furthermore, mZJP upregulated Nrf2 and HO-1 expression levels while downregulating Akt and GSK-3β phosphorylation levels. Notably, the EMT-suppressing effect of mZJP was significantly attenuated upon Nrf2 silencing, as evidenced by enhanced cell migration, decreased epithelial marker expression (E-cadherin), increased mesenchymal marker expression (vimentin and α-SMA), suppression of the Nrf2 pathway, and activation of the Akt/GSK3β pathway.
Conclusion: Our study suggested that RPE protection by mZJP against oxidative stress induced EMT through Nrf2 activation and inhibition of the Akt/GSK3β pathway. MZJP could be a potential candidate drug for the treatment of dry AMD.
Keywords: Akt/GSK3β pathway; Nrf2 pathway; age-related macular degeneration; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; modified ZhuJing pill.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Xiong, Feng, Gao, Zhou, Hui, Zhou, Jin, Shao and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
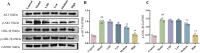
References
-
- Boles N. C., Fernandes M., Swigut T., Srinivasan R., Schiff L., Rada-Iglesias A., et al. (2020). Epigenomic and transcriptomic changes during human RPE EMT in a stem cell model of epiretinal membrane pathogenesis and prevention by nicotinamide. Stem Cell Rep. 14, 631–647. 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.03.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao Y., Ibrahim K. S., Li X., Wong A., Wu Y., Yu X. D., et al. (2023). Chinese medicine, Qijudihuang pill, mediates cholesterol metabolism and regulates gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice, implications for age-related macular degeneration. Front. Immunol. 14, 1274401. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274401 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

