HGF/c-MET axis contributes to CLL cell survival by regulating multiple mechanisms making it a potential therapeutic target for CLL treatment
- PMID: 40520181
- PMCID: PMC12162569
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1612916
HGF/c-MET axis contributes to CLL cell survival by regulating multiple mechanisms making it a potential therapeutic target for CLL treatment
Abstract
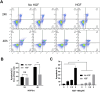
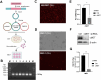
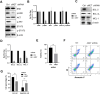
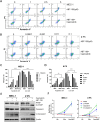
Despite significant advances in understanding the occurrence, progression and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), there remains a need to explore novel mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. In this study, we discovered that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a cytokine highly expressed by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells within the microenvironment, activates the AKT, ERK and STAT3 signaling pathways, promotes the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-2, MCL-1, and BCL-xL, thereby enhancing CLL cell survival and resistance to both natural and ABT-199-induced apoptosis. Knockdown of c-MET, the unique receptor for HGF, using lentivirus-mediated shRNA, significantly attenuated the activation of these pro-survival signaling pathways and downregulated the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins in the BCL-2 family. Consequently, this inhibited CLL cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis. Similarly, pharmacological targeting of the HGF/c-MET pathway with the inhibitor capmatinib markedly suppressed the activation of pro-survival signaling pathways, reduced the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins, inhibited cell proliferation, arrested cell cycle at G0/G1 stage, induced apoptosis, and enhanced the pro-apoptotic effect of ABT-199. In summary, this study highlights the critical role of HGF/c-MET axis in CLL cell survival and demonstrates that targeting this pathway holds therapeutic potential for the treatment of CLL.
Keywords: HGF/c-Met; anti-apoptotic proteins; capmatinib; chronic lymphocytic leukemia; signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Shao, Meng, Cui, Sun, Sun, Zhang, Shen, Qin, Yang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MDM2 inhibitor APG-115 synergizes with ABT-199 to induce cell apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 31;15:1441383. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1441383. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39144622 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and Immunosuppression Induced by Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(1):24-33. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170220095838. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28231754 Review.
-
IFN-γ enhances CLL cell resistance to ABT-199 by regulating MCL-1 and BCL-2 expression via the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway.Leuk Lymphoma. 2023 Jan;64(1):71-78. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2022.2131408. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Leuk Lymphoma. 2023. PMID: 36222521
-
MCL-1 and BCL-xL-dependent resistance to the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 can be overcome by preventing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in lymphoid malignancies.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jan 15;6(1):e1593. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.525. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25590803 Free PMC article.
-
Role of HGF/MET axis in resistance of lung cancer to contemporary management.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012 Sep;1(3):179-93. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2012.09.04. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 25806180 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baljevic M., Zaman S., Baladandayuthapani V., Lin Y. H., de Partovi C. M., Berkova Z., et al. (2017). Phase II study of the c-MET inhibitor tivantinib (ARQ 197) in patients with relapsed or relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Ann. Hematol. 96 (6), 977–985. 10.1007/s00277-017-2980-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

