Oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain in cancer: animal models and related research progress
- PMID: 40520182
- PMCID: PMC12162332
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1609791
Oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain in cancer: animal models and related research progress
Abstract
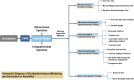
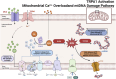
Oxaliplatin, a third-generation platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent, has shown substantial efficacy in cancer treatment. However, its associated side effects, particularly chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathic pain (CIPNP), continue to challenge cancer survivors globally. Clinically, it frequently presents as numbness, coldness, and discomfort in the limbs and extremities. Duloxetine is advised for analgesic purposes. Despite its clinical relevance, both the application methods and the underlying mechanisms of oxaliplatin-induced CINP warrant further investigation. Consequently, more precise animal models are needed to explore the mechanisms and progression of this condition. This review consolidates recent advancements in rat and mouse models of oxaliplatin-induced CINP, with the aim of enhancing modeling success rates and developing models that more accurately mirror disease progression. Such models are essential for advancing clinical research and drug development.
Keywords: CINP animal model; applications; chemotherapy; neuropathic pain; oxaliplatin.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Shi, Wang, Piao, Yao, Yu, Zhai, Liu, Li, Fu, Shen, Jin and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Agnes J. P., Dos Santos B., das Neves R. N., Luciano V. M. M., Benvenutti L., Goldoni F. C., et al. (2023). β-Caryophyllene Inhibits oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice: role of Cannabinoid type 2 receptors, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Antioxidants (Basel) 12 (10), 1893. 10.3390/antiox12101893 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

