Steamed panax notoginseng mitigates CA-MRSA USA300-induced necroptosis in human neutrophils
- PMID: 40520183
- PMCID: PMC12163054
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1546652
Steamed panax notoginseng mitigates CA-MRSA USA300-induced necroptosis in human neutrophils
Abstract
Background: Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) disrupts innate immunity by inducing necroptosis in polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), a process linked to excessive inflammation and tissue damage. CA-MRSA releases virulence factors that enhance its pathogenicity by disrupting the host's innate immune response, particularly impairing the phagocytic function of PMNs. Steamed Panax notoginseng (S-PN), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), has demonstrated immune-regulatory and anti-inflammatory properties, showing promising therapeutic effects in alleviating the severe inflammatory responses induced by pathogenic microbial infections.
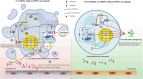
Objective: This study aims to investigate the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of S-PN alleviating CA-MRSA-induced PMN necroptosis by suppressing MRSA virulence factors and inhibiting the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL signaling pathway, thereby attenuating inflammatory damage.
Methods: A co-culture model of MRSA USA300 strain and PMNs isolated from healthy human blood was established to observe the changes in necroptosis marker HMGB1, PMNs counts, ROS, chemokine MCP-1 and pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-8, TNF-α. RNA-seq was employed to analyze the effects of S-PN on the transcriptional expression of pathogenesis-related genes of MRSA. RT-PCR was utilized to validate the expression of S-PN on MRSA virulence factors and PMNs necroptosis related genes.
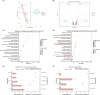
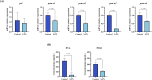
Results: S-PN significantly inhibited HMGB1, ROS, MCP-1, IL-1β and IL-8 in MRSA-PMN co-cultures, the PMN count in the S-PN group was higher than that in the model group. S-PN downregulated MRSA pathogenic-associated S. aureus infection and quorum sensing signaling pathways, and significantly reduced the virulence factors PSM and PVL. S-PN suppressed the expression of genes associated with necroptosis ripk1, ripk3, and mlkl in PMNs.
Conclusion: S-PN alleviates CA-MRSA infection-induced immune damage through dual mechanisms: suppression of bacterial virulence factors (PSM and PVL) and inhibition of PMNs necroptosis. These findings underscore its potential as a complementary therapeutic strategy against CA-MRSA infections, providing a theoretical foundation for integrating TCM into adjuvant treatments for drug-resistant bacterial infections.
Keywords: CA-MRSA; necroptosis; polymorphonuclear neutrophils; steamed Panax notoginseng; virulence factors.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Feng, An, Yang, Xia, Wen, Zheng, Chen, Cheng, Jiang, Lu and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cella M. A., Coulson T., MacEachern S., Badr S., Ahmadi A., Tabatabaei M. S., et al. (2023). Probiotic disruption of quorum sensing reduces virulence and increases cefoxitin sensitivity in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 4373. 10.1038/s41598-023-31474-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

