The role of spontaneous clearance on fractional analysis of HBV
- PMID: 40520250
- PMCID: PMC12167083
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2025.05.009
The role of spontaneous clearance on fractional analysis of HBV
Abstract
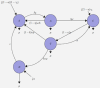
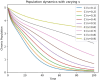
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) remains a persistent global health concern, with recent research advancing our understanding of its transmission dynamics and potential interventions.The present study proposes a mathematical model of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) epidemics using fractional calculus, with a special emphasis on the influence of spontaneous clearance across diverse population groups. Using the Atangana-Baleanu derivative, the model accounts for the complications of vertical and horizontal transmission, therapy, immunisation, and spontaneous clearance. Numerical simulations with different fractional orders demonstrate how spontaneous clearance affects the dynamics of susceptible, chronic, treated, and recovered populations. The findings indicate that in vulnerable populations, increasing spontaneous clearance reduces vulnerability because people either clear the illness naturally or gain resistance.However, in chronic populations, spontaneous clearance is insufficient for complete recovery without treatment. The combination of therapy and spontaneous clearance improves the treated population, demonstrating the beneficial effects of both medical intervention and natural immunity. Furthermore, increased spontaneous clearance boosts the restored population, demonstrating the immune system's ability to eliminate the virus over time. The fractional-order framework captures the memory effect of illness development, revealing how healing is time-dependent and how immune responses have a long-term impact. This study emphasises the need of combining spontaneous clearance with medical therapies to improve HBV management and public health consequences. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) remains a persistent global health concern, with recent research advancing our understanding of its transmission dynamics and potential interventions. This study presents a fractional mathematical model of HBV infection, employing the Atangana-Baleanu derivative with Mittag-Leffler kernels to capture memory-dependent and nonlocal transmission processes. The model integrates vertical and horizontal transmission pathways, treatment strategies, immunization efforts, and spontaneous clearance, providing a nuanced perspective compared to classical models. Stability conditions are analyzed through fixed-point theory, revealing the global stability of both disease-free and endemic states under specific values of the basic reproduction number R 0. Numerical simulations demonstrate the model's effectiveness in capturing the complex dynamics of HBV, with fractional-order parameters enhancing prediction accuracy. This approach offers valuable insights into optimizing public health interventions and treatment strategies for managing HBV infections effectively.
Keywords: Basic reproduction number; Fixed point theory; Fractal fractional model; Hepatitis B virus; Memory-dependent; Stability.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest and funding available for this research
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad S., Ullah A., Ali A., Bayatti H.Al. Theoretical analysis of HBV infection under Mittag-Leffler derivative. Progress in Fractional Differentiation and Applications. 2023;9(1):99–106.
-
- Ain Q.T., Chu Y.-M. On fractal fractional hepatitis B epidemic model with modified vaccination effects. Fractals. 2023;31(10) doi: 10.1142/S0218348X23400066. - DOI
-
- Atangana A., Baleanu D. New fractional derivatives with nonlocal and nonsingular kernel: Theory and application to heat transfer model. Thermal Science. 2016;20(2):763–769.
-
- Baleanu D., Diethelm K., Scalas E., Trujillo J.J. Fractional calculus models and numerical methods. World Scientific. Series on Complexity, Nonlinearity and Chaos. 2012;3
-
- Din A., Abidin M.Z. Analysis of fractional-order vaccinated Hepatitis-B epidemic model with Mittag-Leffler kernels. Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Simulation with Applications. 2022;2(2):59–72. doi: 10.53391/mmnsa.2022.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

