Durable HTT silencing using non-evolved dCas9 epigenome editors in patient-derived cells
- PMID: 40520366
- PMCID: PMC12163160
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102561
Durable HTT silencing using non-evolved dCas9 epigenome editors in patient-derived cells
Abstract
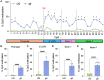
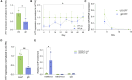
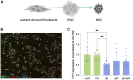
Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by a trinucleotide repeat expansion in exon 1 of the huntingtin (HTT) gene. Nuclease-deficient Cas9 protein (dCas9) epigenetic editing for targeted gene regulation is a promising therapeutic approach for HD through downregulation of the causative gene, HTT. A screen of several dCas9 variants with expanded PAM recognition was fused to KRAB and DNMT3A/L to assess the ability to downregulate total HTT. Surprisingly, only S pdCas9 could significantly downregulate HTT, while expanded PAM recognition variants dxCas9 and dCas9-VQR were less efficient or unable to reduce HTT expression. Using our lead construct with S pdCas9, DNA methylation changes were assessed through reduced representation bisulfite sequencing, showing high on-target increases in DNA methylation and few off-targets. In addition, HTT silencing was mitotically stable for up to 6 weeks in a rapidly dividing cell line. Finally, significant downregulation of HTT was achieved in patient-derived neuronal stem cells, showing the efficacy of this system in a disease-relevant cell type. This approach represents a novel therapeutic pathway for the treatment of HD.
Keywords: CRISPR; DNA methylation; Huntington’s disease; MT: RNA/DNA Editing; dCas9; epigenetics.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Kremer B., Goldberg P., Andrew S.E., Theilmann J., Telenius H., Zeisler J., Squitieri F., Lin B., Bassett A., Almqvist E. A Worldwide Study of the Huntington’s Disease Mutation: The Sensitivity and Specificity of Measuring CAG Repeats. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;330:1401–1406. - PubMed
-
- Bates G.P. The molecular genetics of Huntington disease — a history. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:766–773. - PubMed
-
- Davies S.W., Turmaine M., Cozens B.A., DiFiglia M., Sharp A.H., Ross C.A., Scherzinger E., Wanker E.E., Mangiarini L., Bates G.P. Formation of Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusions Underlies the Neurological Dysfunction in Mice Transgenic for the HD Mutation. Cell. 1997;90:537–548. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

