Age of onset, treatment response, and survival rates in Dutch Kooiker dogs diagnosed with hereditary polymyositis
- PMID: 40520426
- PMCID: PMC12163053
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1559040
Age of onset, treatment response, and survival rates in Dutch Kooiker dogs diagnosed with hereditary polymyositis
Abstract
Introduction: Hereditary polymyositis in Kooiker dogs is genetically linked to the deletion of a 39 kb DNA fragment located 10 kb upstream of the interleukin IL21/IL2 locus, exhibiting low penetrance. This study aims to identify prognostic factors for Kooiker dogs that are affected and evaluate three treatments: (1) glucocorticoid monotherapy, (2) glucocorticoids combined with supplements (vitamin B, L-carnitine, and coenzyme Q10), and (3) glucocorticoids combined with supplements and oclacitinib.
Method: This study incorporates both retrospective and prospective designs. A total of 97 Kooiker dogs diagnosed with histopathologically confirmed polymyositis, or those showing clinical signs consistent with polymyositis and homozygous or heterozygous for a 39-kb deletion, were included. Dogs seen before the end of 2006 received only Treatment 1, those identified between 2007 and 2015 received Treatment 2, and those seen after 2015 received Treatment 3. A dataset was created that included sex, neuter status, age of onset (AoO), the 39 kb deletion, clinical signs, treatment, creatinine kinase (CK) activity at diagnosis and during follow-up visits, owner-reported improvement during treatment, cause of death, and date of death. Descriptive statistics and Cox proportional hazards survival analysis were conducted to examine factors influencing age of onset, treatment response, and survival.
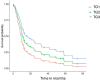
Results: The 39 kb deletion showed no association with clinical signs or creatine kinase (CK) activity at diagnosis. However, homozygous Kooiker dogs with the 39 kb deletion had a lower AoO. A significant decrease in CK activity was observed in 18 dogs during the first recheck after treatment, and most owners reported clinical improvement following the start of treatment. The type of treatment influenced survival time, with dogs treated with glucocorticoids, supplements, and oclacitinib having the longest survival.
Discussion: A treatment regimen that included glucocorticoids, supplements, and oclacitinib was the most effective in this study, although it was not statistically significant.
Keywords: L-carnitine; apoquel; coenzyme Q10; myopathy; oclacitinib; prednisolone; treatment; vitamin B.
Copyright © 2025 Opmeer, Alf, Leegwater, Fieten and Mandigers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polymyositis in Kooiker dogs is associated with a 39 kb deletion upstream of the canine IL21/IL2 locus.PLoS Genet. 2025 Jan 2;21(1):e1011538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011538. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 39746095 Free PMC article.
-
Pathologic Changes in and Immunophenotyping of Polymyositis in the Dutch Kooiker Dog.Animals (Basel). 2024 Aug 29;14(17):2519. doi: 10.3390/ani14172519. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272303 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of oclacitinib (Apoquel®) compared with prednisolone for the control of pruritus and clinical signs associated with allergic dermatitis in client-owned dogs in Australia.Vet Dermatol. 2014 Dec;25(6):512-8, e86. doi: 10.1111/vde.12166. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Vet Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25109820 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety of the Selective JAK1 Inhibitor Oclacitinib in Dogs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2025 May;48(3):135-145. doi: 10.1111/jvp.13503. Epub 2025 Feb 28. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40018984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mandigers F, Karelse JJHGD. Blauwgoed, helen en halven,100 jaar ringwerk in eendenkooien Werkgroep Ringwerk Eendenkooien Nederland. Dalfsen, The Netherlands: WREN (2013).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

