Yogic Bellows, Neural Sparks: Unravelling the Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Kapalbhati-A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40520439
- PMCID: PMC12162548
- DOI: 10.1177/09727531251340154
Yogic Bellows, Neural Sparks: Unravelling the Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Kapalbhati-A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Kapalbhati is a dynamic yogic breathing technique characterised by rapid, forceful exhalations followed by passive inhalations. Traditionally celebrated for detoxification, enhanced pulmonary function and improved mental clarity, its underlying neurophysiological mechanisms remain largely speculative.
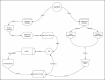
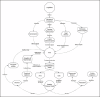
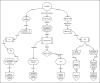
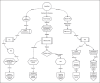
Summary: This systematic review synthesises evidence from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) on Kapalbhati's effects on respiratory and cognitive outcomes, and proposes a hypothetical integrative model to advance our understanding of this ancient practice. A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, ScienceDirect and the Cochrane Library using keywords such as "Kapalbhati," "skull shining breath" and related synonyms. Only English-language RCTs published between 2014 and 2024 were included. Four RCTs meeting these criteria were critically appraised and their findings synthesised. The reviewed studies consistently indicate that Kapalbhati improves pulmonary function, possibly by mechanically stimulating pulmonary stretch receptors, and enhances cognitive performance by reducing anxiety and boosting attention. These outcomes suggest that the rapid breathing of Kapalbhati may modulate neural circuits in the nucleus tractus solitarius, thereby triggering the release of neuropeptides like oxytocin and norepinephrine, which are essential for emotional regulation and cognitive enhancement.
Key message: Integrating traditional yogic insights with contemporary neurophysiological theories, our proposed model offers a fresh perspective on Kapalbhati's multifaceted benefits. This review not only highlights promising empirical findings but also lays the groundwork for future research aimed at validating these mechanisms and potentially transforming Kapalbhati into an evidence-based therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: Pranayama; Yogic breathing; cognition; emotional regulation; respiratory function.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Analysis of the Effects of Exercise and Kapalbhati Pranayama on Heart Rate Variability and Electroencephalogram Activity: Unveiling Physiological and Cognitive Insights.Mymensingh Med J. 2024 Jul;33(3):897-907. Mymensingh Med J. 2024. PMID: 38944738
-
Effects of Various Prāṇāyāma on Cardiovascular and Autonomic Variables.Anc Sci Life. 2016 Oct-Dec;36(2):72-77. doi: 10.4103/asl.ASL_178_16. Anc Sci Life. 2016. PMID: 28446827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of yogic breath regulation: A narrative review of scientific evidence.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2019 Jan-Mar;10(1):50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2017.07.008. Epub 2018 Feb 1. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 29395894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effectiveness of Integrated Care Pathways for Adults and Children in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(3):80-129. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907030-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27820426
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patra S. Physiological effect of kriyas: Cleansing techniques. Int J Yoga - Philos Psycholo Parapsychol 2017; 5: 3.
-
- Mishra S and Dash SC.. An overview of Hatha yogic practices in Hatha yoga Pradipika, Gheranda Samhita and Shiva Samhita. Res J Humanities Soc Sci 2017; 8: 354.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

