Changes After Leptin Administration in Partial Lipodystrophy and Factors Associated With Hepatic and Metabolic Response
- PMID: 40520449
- PMCID: PMC12164294
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf067
Changes After Leptin Administration in Partial Lipodystrophy and Factors Associated With Hepatic and Metabolic Response
Abstract
Context: Partial lipodystrophy (PL) is a rare disease characterized by selective loss of subcutaneous fat.
Objective: To evaluate changes in apolipoproteins, hepatokines, hormones, appetite regulators, and inflammatory markers in patients with PL treated with leptin, assess postprandial metabolism and 24-hour dynamics, and identify predictors of hepatic and metabolic response to therapy.
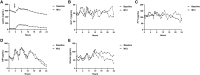
Methods: We studied 19 subjects from our previous clinical study (NCT01679197), which investigated the effect of leptin on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis associated with PL. A mixed-meal test was performed in a subgroup of 14 patients, and paired 24-hour frequent sampling with standardized meals was completed in 5 individuals.
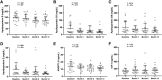
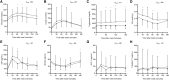
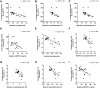
Results: Leptin treatment led to reductions in apolipoproteins B, CII, CIII, and E (P < .05). Levels of ANGPTL3 tended to decrease after leptin treatment (P = .079). The mixed-meal test revealed significant reductions in triglyceride area under the curve (P = .017) and glucose excursions at several postmeal time points (P < .05). The immediate GIP secretion in response to a meal attenuated after leptin therapy (P = .005 at 60 minutes). Ghrelin levels showed an increase after leptin administration. The response to leptin treatment was associated with several factors, including baseline carbohydrate intake, leptin and triglyceride levels and triglyceride-rich apolipoproteins, and changes in triglyceride-rich apolipoproteins (P < .05 for all). Changes in IGF-1 levels were correlated with improvements in metabolic and liver parameters (P < .05).
Conclusion: Leptin therapy modulates lipid metabolism, postprandial glucose regulation, and appetite signaling in patients with PL, with responses associated with metabolic parameters and carbohydrate intake.
Keywords: MASH; incretins; leptin; partial lipodystrophy; response.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Chan JL, Oral EA. Clinical classification and treatment of congenital and acquired lipodystrophy. Endocr Pract. 2010;16(2):310‐323. - PubMed
-
- Akinci B, Meral R, Oral EA. Phenotypic and genetic characteristics of lipodystrophy: pathophysiology, metabolic abnormalities, and comorbidities. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(12):143. - PubMed
-
- Garg A, Misra A. Lipodystrophies: rare disorders causing metabolic syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004;33(2):305‐331. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
