Association of neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio with mortality in older stroke survivors
- PMID: 40520535
- PMCID: PMC12162721
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1611289
Association of neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio with mortality in older stroke survivors
Abstract
Background: The neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio (NPAR) functions as an integrative marker representing inflammatory response and nutritional health. However, its association with mortality in elderly stroke survivors has not been explored.
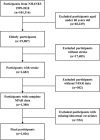
Methods: This cohort study analyzed data from 1,026 elderly stroke survivors in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES, 1999-2018). The association of NPAR with mortality was analyzed using Cox proportional hazards regression, restricted cubic splines (RCS), Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, and time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Subgroup analyses and interaction tests were also performed.
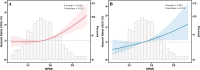
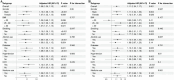
Results: During the 6.65-year median follow-up, elevated NPAR showed independent associations with increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Quartile-based analysis revealed 69 and 87% greater mortality hazards for the highest versus lowest NPAR groups, respectively. RCS analysis revealed a non-linear threshold effect at NPAR = 14.5, beyond which the risk of all-cause mortality increased sharply. NPAR demonstrated stable predictive accuracy, with time-dependent AUC ranging from 0.664 to 0.607 for all-cause mortality and 0.652-0.609 for cardiovascular mortality over 3-10 years. Subgroup analyses confirmed consistency across different sex, BMI, lifestyle habits, and comorbidity categories.
Conclusion: This study underscores a strong positive correlation between NPAR and prognosis in older adult stroke survivors in the United States, indicating its potential as a novel biomarker for prognostic assessment.
Keywords: NHANES; NPAR; elderly; mortality; stroke survivors.
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Zhang, Ding, Yu and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
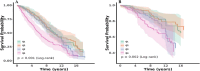

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

