Nerve growth factor-loaded biomimetic prussian blue nanocomplexes for reversing osteoporosis via promoting osteoblast precursor cell proliferation and differentiation
- PMID: 40520557
- PMCID: PMC12166439
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101898
Nerve growth factor-loaded biomimetic prussian blue nanocomplexes for reversing osteoporosis via promoting osteoblast precursor cell proliferation and differentiation
Abstract
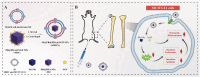
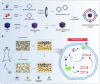
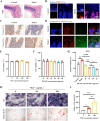
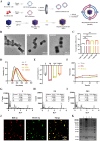
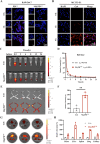
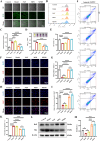
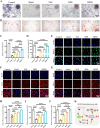
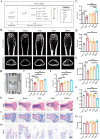
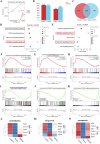
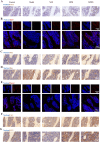
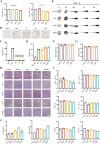
The fundamental issue of osteoporosis (OP) is osteoblast decrease due to oxidative stress and the subsequent disruption of the osteogenic and osteoclastic dynamic balance. How to promote the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of osteoblast precursor cells (MC3T3-E1) in an oxidative microenvironment is a great challenge for improving OP. In this study, Prussian blue nanoparticles (PB NPs) were initially functionalized with a polydopamine (PDA) coating. Nerve growth factor (NGF) was subsequently immobilized on the PDA layer, followed by the hybrid membrane coating composed of red blood cell membrane (RBCm) and MC3T3-E1 cell membrane (MC3T3m), thereby constructing a biomimetic Prussian blue nanocomplex loaded with NGF (MPDN NPs). In vitro studies have shown that the nanodrug restored the impaired proliferation viability of MC3T3-E1 cells and inhibit their apoptosis by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), and further cooperate with NGF to promote osteogenic differentiation. In vivo studies have demonstrated that the nanodrug significantly inhibited bone loss and promote bone regeneration in osteoporotic mice. Moreover, this nanodrug with excellent safety both in vitro and in vivo showed the long half-life in the bloodstream and high accumulation in the bone. In summary, this strategy addresses the fundamental issue of decreased osteoblast in OP and offers a novel approach for preventing and treating OP.
Keywords: Nerve growth factor; Osteoblast precursor cells; Osteogenic differentiation; Osteoporosis; Prussian blue nanoparticles; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nerve growth factor promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells via BMP-2/Smads pathway.Ann Anat. 2022 Jan;239:151819. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2021.151819. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Ann Anat. 2022. PMID: 34391912
-
Ophiopogonin D: A new herbal agent against osteoporosis.Bone. 2015 May;74:18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25582622
-
Modulation of the microRNA-6089/E2F transcription factor2 axis by querceting: implications for osteoblast viability, proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation in fracture healing.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024 Apr;75(2):173-183. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2024.2.06. Epub 2024 May 6. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38736264
-
Polydopamine-coated biomimetic bone scaffolds loaded with exosomes promote osteogenic differentiation of BMSC and bone regeneration.Regen Ther. 2023 Mar 30;23:25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2023.03.005. eCollection 2023 Jun. Regen Ther. 2023. PMID: 37063095 Free PMC article.
-
Thiol-Functionalized, Antioxidant, and Osteogenic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Osteoporosis.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023 Jun 12;9(6):3535-3545. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c00479. Epub 2023 May 12. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023. PMID: 37172017
References
-
- Compston J.E., McClung M.R., Leslie W.D. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393(10169):364–376. - PubMed
-
- Xiao P.L., Cui A.Y., Hsu C.J., Peng R., Jiang N., Xu X.H., Ma Y.G., Liu D., Lu H.D. Global, regional prevalence, and risk factors of osteoporosis according to the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2022;33(10):2137–2153. - PubMed
-
- Zhang C., Li H., Li J., Hu J., Yang K., Tao L. Oxidative stress: a common pathological state in a high-risk population for osteoporosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023;163 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

