Multifunctional injectable hydrogel incorporating EGCG-Cu complexes for synergistic antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and osteogenic therapy in periodontitis
- PMID: 40520560
- PMCID: PMC12164233
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101907
Multifunctional injectable hydrogel incorporating EGCG-Cu complexes for synergistic antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and osteogenic therapy in periodontitis
Abstract
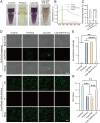
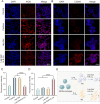
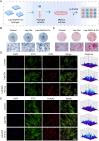
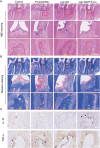
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by oxidative stress, immune system imbalance, and the progressive destruction of periodontal tissues. Traditional treatment approaches are limited by the incomplete eradication of pathogens, the risk of antibiotic resistance, inadequate control of inflammation and oxidative stress, and restricted tissue regeneration capacity. Therefore, this study proposes an injectable multifunctional Laponite/gelatin hydrogel loaded with epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)-copper ion (Cu2+) complexes as a localized therapy for periodontitis. EGCG exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties; however, its clinical application is hindered by poor stability and bioavailability. Cu2+ coordination enhances EGCG stability and antioxidant capacity while improving its antimicrobial efficacy. Experimental results demonstrate that the Laponite/gelatin hydrogel is adaptable for the localized delivery of EGCG-Cu, with bioactive metal ions such as Li+, Mg2+, and Si4+ contained in Laponite, which promote osteogenesis and periodontal tissue regeneration. In vitro and in vivo studies confirm that this hydrogel exhibits excellent biocompatibility, effectively inhibits Porphyromonas gingivalis, suppresses M1 polarization while promoting M2 polarization, and facilitates periodontal tissue repair. Therefore, this study provides promising insights into a localized therapeutic strategy for periodontitis.
Keywords: Alveolar bone regeneration; Copper ions (Cu2+); Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG); Hydrogel; Periodontitis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







Similar articles
-
ZIF-8 modified multifunctional injectable photopolymerizable GelMA hydrogel for the treatment of periodontitis.Acta Biomater. 2022 Jul 1;146:37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.03.046. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35364317
-
ROS scavenging and immunoregulative EGCG@Cerium complex loaded in antibacterial polyethylene glycol-chitosan hydrogel dressing for skin wound healing.Acta Biomater. 2023 Aug;166:155-166. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.027. Epub 2023 May 23. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37230435
-
Synergistic Effects of Shed-Derived Exosomes, Cu2+, and an Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel on Antibacterial, Anti-inflammatory, and Osteogenic Activity for Periodontal Bone Regeneration.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Jul 3;16(26):33053-33069. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c05062. Epub 2024 Jun 20. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38899855
-
New Insights in Natural Bioactive Compounds for Periodontal Disease: Advanced Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Molecules. 2025 Feb 10;30(4):807. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040807. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The recent progress of bone regeneration materials containing EGCG.J Mater Chem B. 2024 Oct 9;12(39):9835-9844. doi: 10.1039/d4tb00604f. J Mater Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39257355 Review.
References
-
- Ge X., Hu J., Qi X., Shi Y., Chen X., Xiang Y., et al. An immunomodulatory hydrogel featuring antibacterial and reactive oxygen species scavenging properties for treating periodontitis in diabetes. Adv. Mater. 2025;37 - PubMed
-
- Chen X., Huang N., Wang D., Zhang M., Deng X., Guo F., et al. Sulfated chitosan-modified CuS nanocluster: a versatile nanoformulation for simultaneous antibacterial and bone regenerative therapy in periodontitis. ACS Nano. 2024;18:14312–14326. - PubMed
-
- Ming P., Li B., Li Q., Yuan L., Jiang X., Liu Y., et al. Multifunctional sericin-based biomineralized nanoplatforms with immunomodulatory and angio/osteo-genic activity for accelerated bone regeneration in periodontitis. Biomaterials. 2025;314 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

