The clinical efficacy and mechanism of gamma frequency electroacupuncture stimulation on the rehabilitation of upper limb motor function in stroke patients: study protocol of a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 40520615
- PMCID: PMC12162516
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1603522
The clinical efficacy and mechanism of gamma frequency electroacupuncture stimulation on the rehabilitation of upper limb motor function in stroke patients: study protocol of a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The field of neuroscience has discovered that gamma oscillations (30-100 Hz) in the brain play a key role in neuroplasticity, information conduction and neuroprotective mechanisms. Electroacupuncture stimulation (ES) is a modern treatment method that combines the advantages of Chinese acupuncture with those of electrical stimulation, and is widely used in the field of stroke rehabilitation. At present, there is a lack of research on the clinical efficacy and mechanism of applying gamma frequency (40-Hz) ES, a new neuromodulation mode of integrated Chinese and Western medicine, to induce gamma oscillations and promote the rehabilitation of upper limb motor function in stroke patients.
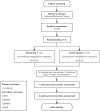
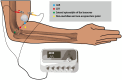
Methods and analysis: This trial uses a randomized, double-blind and controlled method to evaluate the effect of 40-Hz ES of LI11 (Quchi) acupoint on upper limb motor functional rehabilitation in stroke patients. Based on this new rehabilitation program combining Traditional Chinese medicine with modern technique, all patients will receive baseline assessment, 1-week post-intervention assessment and 2-week post-intervention assessment. The primary outcomes are the Fugl-Meyer Assessment Upper Extremity Scale. The secondary indicators include electroencephalogram, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, Mini-mental State Examination and Modified Barthel Index.
Discussion: This trial offers novel perspectives on the application of 40-Hz electroacupuncture stimulation in neural oscillation regulation and the effectiveness of this clinically widespread technique in treating upper extremity dysfunction after a stroke and improving patients' quality of life. The results of this study will contribute to the scientific community's understanding of the potential mechanisms of this novel neuromodulation method, including changes in neural network connectivity, and improve existing clinical treatments to benefit more stroke patients.
Clinical trial registration: https://www.chictr.org.cn/showprojEN.html?proj=217786, identifier ChiCTR2400082208.
Keywords: electroacupuncture stimulation; gamma oscillations; neurological recovery; stroke; upper limb motor function.
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Yu, Ma, Lai, Wu, Zhang, Zhang, Luo, Fu, Feng, Hu, Shan, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gamma oscillations induced by 40-Hz visual-auditory stimulation for the treatment of acute-phase limb motor rehabilitation after stroke: study protocol for a prospective randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Apr 26;25(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08121-w. Trials. 2024. PMID: 38671516 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acupuncture synchronized rehabilitation therapy on upper limb motor and sensory function after stroke: a study protocol for a single-center, 2 × 2 factorial design, randomized controlled trial.Front Neurol. 2023 Sep 28;14:1162168. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1162168. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37840941 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and mechanisms of synchronous virtual reality action observation and electrical stimulation on upper extremity motor function and activities of daily living in patients with stroke: a protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 4;16:1499178. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1499178. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40255890 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal acupuncture methods for lower limb motor dysfunction after stroke: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1415792. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1415792. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39055317 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Method of Electrical Stimulation for the Treatment of Upper Limb Dysfunction After Stroke: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Sep 15;17:2937-2954. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S332967. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 34552328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

