The value of nanocarbon contrast methylene blue based on dye-based tracer technology in sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40520631
- PMCID: PMC12166851
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19546
The value of nanocarbon contrast methylene blue based on dye-based tracer technology in sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare the diagnostic value of nanocarbon suspensions and methylene blue injections in sentinel lymph node biopsies of patients with breast cancer based on the dye method.
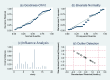
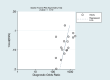
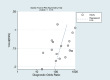
Methods: A systematic search of the PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library (Central) and Web of Science (SCI Expanded) databases was performed to determine the diagnostic value of carbon nanoparticles in Chinese databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), VIP, Wanfang, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM)) for identifying methylene blue in sentinel lymph node biopsies of patients with breast cancer. The QUADAS2 quality evaluation tool of Review Manager 5.4 was used to evaluate the quality of the included studies. Meta-Disc 1.4 software was used to calculate the extracted valid data and perform a heterogeneity test. STATA 14.0 software was selected to conduct a sensitivity analysis, and Deek's publication bias test was used for the included studies.
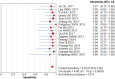
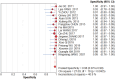
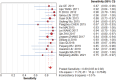
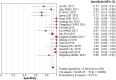
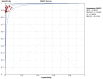
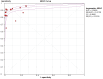
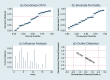
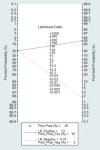
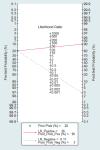
Results: In 17 articles, the binding sensitivity of nanocarbons was 0.93 (0.90-0.95), the binding specificity was 0.98 (0.97-0.99), the binding sensitivity of methylene blue was 0.89 (0.85-0.92), and the binding specificity was 0.94 (0.92-0.95). The AUC value of the nanocarbon SROC was 0.9827 (SE = 0.0062), and the AUC value of methylene blue was 0.9495 (SE = 0.0139).
Conclusion: Nanocarbon versus methylene blue is a more satisfactory dye tracer for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients and should be considered a first-line diagnostic agent.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Diagnostic value; Methylene blue; Nanocarbon suspension.
©2025 Xia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sentinel lymph node biopsy in early stage ovarian cancer: A prospective observational study.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2025 Apr 17;308:121-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2025.02.062. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2025. PMID: 40043529
-
Positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Jan;15(4):iii-iv, 1-134. doi: 10.3310/hta15040. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21276372 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analyses of sentinel lymph node identification in breast cancer and melanoma, a plea for tracer mapping.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016 Apr;42(4):466-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2015.12.007. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26853759
-
Carbon dye versus indocyanine green for sentinel lymph node mapping in endometrial cancer: a prospective dual-center study.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2025 Jun;35(6):101749. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgc.2025.101749. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40180815
-
Radiocolloid-based dynamic sentinel lymph node biopsy in penile cancer with clinically negative inguinal lymph node: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Dec;48(12):2001-2013. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1405-x. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27577753
References
-
- Aziz HK, Azhar Y, Widarda IR, Abdurahman M, Erdiansyah Z, Nugraha P, Lukman K. Accuracy rate of methylene blue injection in sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer patients: a prospective observational study. Breast Cancer. 2023;1:15891–15897. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S439325. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bove S, Fragomeni SM, Romito A, Di Giorgio D, Rinaldi P, Pagliara D, Verri D, Romito I, Paris I, Tagliaferri L, Marazzi F, Visconti G, Franceschini G, Masetti R, Garganese G. Techniques for sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. Minerva Surgery. 2021;76:550–563. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5691.21.09002-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brahma B, Putri RI, Karsono R, Andinata B, Gautama W, Sari L, Haryono SJ. The predictive value of methylene blue dye as a single technique in breast cancer sentinel node biopsy: a study from Dharmais Cancer Hospital. World Journal of Surgical Oncology. 2017;15:41. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1113-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

