Current developments of metal- and metalloid-based quinoline compounds as leishmanicidal agents
- PMID: 40520680
- PMCID: PMC12162633
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1586044
Current developments of metal- and metalloid-based quinoline compounds as leishmanicidal agents
Abstract
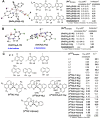
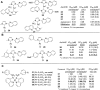
The quinoline moiety represents an important scaffold for the development of leishmanicidal agents. In particular, its hybridization with metal/metalloids has generated highly active compounds that are, in some cases, highly selective against leishmaniasis models. The existing leishmanicidal metal-/metalloid-quinoline compounds are mainly based on the following: (i) coordination compounds based on 8-hydroxyquinolinate; (ii) metallocene derivatives; (iii) N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes featuring a quinoline moiety. This mini-review summarizes the reported cases of leishmanicidal metal and metalloid-based quinoline compounds for each group (i-iii), focusing on the structure-property relationship from in vitro Leishmania models and mechanisms of action, in vivo experiments, and pharmacokinetic data, if available. This paper aims to describe the state of the art of inorganic medicinal chemistry for the development of selective and potent leishmanicidal agents using the quinoline moiety.
Keywords: 8-quinolinate; Leishmania; N-heterocyclic carbenes; ferrocene; quinoline.
Copyright © 2025 Del Carpio, Hernández, Lubes, Jourdan, Cerecetto, Scalese, Gambino and Romero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comprehensive revision on the use of quinoline antimalarial drugs as leishmanicidal agents.Front Chem. 2025 May 30;13:1608340. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1608340. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40520678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, leishmanicidal activity, structural descriptors and structure-activity relationship of quinoline derivatives.Future Med Chem. 2018 Sep 1;10(17):2069-2085. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0124. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Future Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30066582
-
4-Aminoquinoline as a privileged scaffold for the design of leishmanicidal agents: structure-property relationships and key biological targets.Front Chem. 2025 Jan 29;12:1527946. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1527946. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 39981131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and antileishmanial activities of gold(I) complexes involving quinoline functionalized N-heterocyclic carbenes.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Apr 13;94:22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.02.046. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25747497
-
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Coinage Metal Complexes of the Germanium-Rich Metalloid Clusters [Ge₉R₃]- and [Ge₉RI₂]²- with R = Si(iPr)₃ and RI = Si(TMS)₃.Molecules. 2017 Jul 19;22(7):1204. doi: 10.3390/molecules22071204. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28753928 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Application of nano and microformulations to improve the leishmanicidal response of quinoline compounds: a brief review.Front Chem. 2025 Jul 25;13:1622566. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1622566. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40785709 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aronson N., Herwaldt B. L., Libman M., Pearson R., Lopez-Velez R., Weina P., et al. (2016). Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA) and the American society of tropical medicine and hygiene (ASTMH). Clin. Inf. Dis. 63, 1539–1557. 10.1093/cid/ciw742 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Avanzo R. E., Garcia-Linares G., Rodriguez N., Romero A. H. (2025). A comprehensive revision on the use of quinoline antimalarial drugs as leishmanicidal agents. Front. Chem. 13. 10.3389/fchem.2025.1608340 - DOI
-
- Braga S. (2022). Ruthenium complexes, an emerging class of leishmanicidal drug candidates. Appl. Biosci. 1, 129–142. 10.3390/applbiosci1020009 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

