Kang Ru enhances paclitaxel's efficacy against breast cancer progression
- PMID: 40520866
- PMCID: PMC12163460
- DOI: 10.62347/XMGX2636
Kang Ru enhances paclitaxel's efficacy against breast cancer progression
Abstract
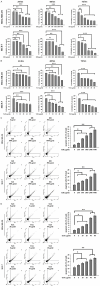
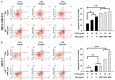
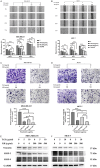
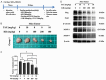
Breast cancer and its associated drug resistance present significant clinical challenges. From a translational medicine perspective, Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine (TCHM) offers promising integrative approach to bridge the experimental findings with clinical application, enhancing cancer treatment outcomes and mitigate drug resistance. In this study, we evaluated a TCM herbal formulation, Kang Ru (KR), comprising Artemisia argyi, Ohwia caudata, and Scoparia dulcis Linn, each traditionally and experimentally recognized for their potential therapeutic properties. We aimed to evaluate the anti-cancer effects of KR on breast cancer and its potential to enhance the efficacy of the chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel. Using breast cancer cell lines we evaluated the effects of KR, both alone and in combination with paclitaxel on cell growth, viability, migration, and invasion. We further evaluated the potential of KR in enhancing paclitaxel to reduce tumor progression using a breast cancer xenograft model in mice. Our findings demonstrated that KR significantly inhibited cell growth and migration in breast cancer cell lines. Moreover, the combination of KR with paclitaxel demonstrated synergistic effects, effectively reducing cell viability, inducing cell apoptosis and inhibiting cell migration. In an animal model, the combination of KR and paclitaxel significantly enhanced breast cancer suppression, corroborating the in vitro findings. In conclusion, KR is a novel Chinese herbal formulation, with significant anti-cancer potential, enhancing paclitaxel's efficacy in inhibiting breast cancer progression. These findings suggest that KR could be a promising adjunctive strategy to improve breast cancer treatment and warrant further translational research to facilitate its clinical development as a complementary therapeutic option.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Kang Ru; drug efficacy; herbal formulation; paclitaxel.
AJCR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancing Chemotherapy Efficacy: Investigating the Synergistic Impact of Paclitaxel and cd73 Gene Suppression on Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration.Cureus. 2024 Jul 21;16(7):e65027. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65027. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39165432 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of erbB3 with MM-121/SAR256212 enhances antitumor activity of paclitaxel against erbB2-overexpressing breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R101. doi: 10.1186/bcr3563. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24168763 Free PMC article.
-
Low doses of paclitaxel enhance liver metastasis of breast cancer cells in the mouse model.FEBS J. 2016 Aug;283(15):2836-52. doi: 10.1111/febs.13767. Epub 2016 Jun 16. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 27307301
-
Paclitaxel's Mechanistic and Clinical Effects on Breast Cancer.Biomolecules. 2019 Nov 27;9(12):789. doi: 10.3390/biom9120789. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31783552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor effect of traditional Chinese herbal medicines against lung cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2014 Oct;25(9):983-91. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000127. Anticancer Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24892722 Review.
References
-
- Xu B, Li H, Jiang Z, Gu L, Tang J, Xie H, Pan Y, Liu Y, Cui S, Wang X, Cai L, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Shao Z. Adjuvant tamoxifen switched to exemestane treatment in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer: a pragmatic, multicenter, and prospective clinical trial in China. Chin J Cancer Res. 2022;34:592–600. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Trayes KP, Cokenakes SEH. Breast cancer treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2021;104:171–178. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
