Efficacy and toxicity of PD-1 inhibitor combined with induction chemotherapy for locally advanced laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers
- PMID: 40520879
- PMCID: PMC12163456
- DOI: 10.62347/HVRH6856
Efficacy and toxicity of PD-1 inhibitor combined with induction chemotherapy for locally advanced laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy, toxicity, and voice rehabilitation outcomes of PD-1 inhibitors combined with induction chemotherapy (PCIC) compared to induction chemotherapy (IC) alone.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 250 patients with stage III/IVA squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx/hypopharynx treated between June 2021 and December 2023. After 1:1 propensity score matching, 216 patients (108 per group) were analyzed. Both groups received platinum-based induction chemotherapy, with the PCIC group receiving an additional PD-1 inhibitor, toripalimab. Efficacy was evaluated based on response rates and survival outcomes, while toxicity profiles and voice rehabilitation were assessed.
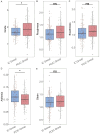
Results: The PCIC group had significantly higher complete remission rates (81.48% vs. 65.74%; P = 0.021) and improved 1-year overall survival (62.96% vs. 49.07%; P = 0.040). The incidence of neutropenia and nausea was higher in the PCIC group (P < 0.05). Voice quality assessments showed worse objective vocal grade but better patient-perceived vocal quality in the PCIC group (both P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The combination of PD-1 inhibitors with induction chemotherapy improve remission rates and survival in patients with locally advanced laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers. However, increased toxicity and voice rehabilitation challenges highlight the need for comprehensive patient support during treatment.
Keywords: PD-1 inhibitors; hypopharyngeal cancer; induction chemotherapy; laryngeal cancer; survival outcomes; toxicity profiles.
AJCR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction Toripalimab and Chemotherapy for Organ Preservation in Locally Advanced Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal Cancer: A Single-Arm Phase II Clinical Trial.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 17;30(2):344-355. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-2398. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 37955629 Clinical Trial.
-
PD-1 Inhibitors combined with paclitaxel (Albumin-bound) and cisplatin for larynx preservation in locally advanced laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective study.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Dec;72(12):4161-4168. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03550-z. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37804437 Free PMC article.
-
Induction chemotherapy for locally advanced laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer: Single institution experience.Head Neck. 2020 Nov;42(11):3118-3124. doi: 10.1002/hed.26353. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Head Neck. 2020. PMID: 32671892
-
Laryngeal Preservation Strategies in Locally Advanced Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal Cancers.Front Oncol. 2019 May 31;9:419. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00419. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31214491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 14;12(12):CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 30;4:CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub3. PMID: 33316104 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Álvarez-Marcos C, Vicente-Benito A, Gayol-Fernández Á, Pedregal-Mallo D, Sirgo-Rodríguez P, Santamarina-Rabanal L, Llorente JL, López F, Rodrigo JP. Voice outcomes in patients with advanced laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer treated with chemo-radiotherapy. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2022;42:243–249. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Echanique KA, Evans LK, Han AY, Chhetri DK, St John MA. Cancer of the larynx and hypopharynx. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2021;35:933–947. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources