Unraveling the Role of N6-Methylation Modification: From Bone Biology to Osteoporosis
- PMID: 40520903
- PMCID: PMC12163421
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.108763
Unraveling the Role of N6-Methylation Modification: From Bone Biology to Osteoporosis
Abstract
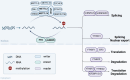
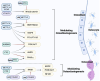
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant and reversible epitranscriptomic modification in eukaryotes, playing a pivotal role in regulating various RNA metabolic processes, including splicing, nuclear export, translation and degradation. Emerging evidence indicates that m6A modification is indispensable in biological processes of bone cells such as proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Given its pivotal influence on osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis, m6A modification, particularly via METTL3, has attracted considerable attention in osteoporosis (OP). In this review, we probe the function of m6A modification in intramembranous and endochondral ossification. Furthermore, we summarize the regulatory role of m6A modification in various biological processes in osteoblasts, osteoclasts and osteocytes, focusing on its potential signaling pathways in osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Specifically, m6A modulates osteoblast differentiation predominantly through signaling pathways such as Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/AKT, and BMP/Smad. Concurrently, it regulates osteoclast differentiation and maturation via the RANKL/RANK pathway and its downstream signaling mechanisms. We also discuss recent discoveries that m6A modification regulates OP and further explore its potential clinical value in diagnosing and treating OP. Collectively, m6A modification serves as a crucial regulatory factor in bone metabolism, and a comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms of m6A modification in bone biology is expected to provide new targets for treating OP.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; bone cells; bone development; m6A modification; osteoporosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
m6A Methylation Regulates Osteoblastic Differentiation and Bone Remodeling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 21;9:783322. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.783322. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34993198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Osteoporosis: Exploring the Power of m6A RNA Modification.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jan;29(1):e70344. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70344. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39779466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chinese Ecliptae herba (Eclipta prostrata (L.) L.) extract and its component wedelolactone enhances osteoblastogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via targeting METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Aug 10;312:116433. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116433. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37004744
-
Study on the Mechanism of Xianling Gubao Capsule Regulating Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 (RUNX2) and Promoting Osteoblast Differentiation by N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) Methyltransferase-Like 3 (METTL3).Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Jun 28:AT10075. Online ahead of print. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38940781
-
METTL3-mediated m6A modification of circSTAT6 modulates miR-188-3p/Beclin1 axis to promote osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Mar 26;20(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05720-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40134002 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal METTL14 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by regulating BMP2 in bone fracture recovery.Hum Cell. 2025 Aug 12;38(5):141. doi: 10.1007/s13577-025-01271-2. Hum Cell. 2025. PMID: 40794239
References
-
- Skvortsova K, Iovino N, Bogdanović O. Functions and mechanisms of epigenetic inheritance in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:774–90. - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Salmon-Divon M, Amariglio N, Rechavi G. Transcriptome-wide mapping of N(6)-methyladenosine by m(6)A-seq based on immunocapturing and massively parallel sequencing. Nat Protoc. 2013;8:176–89. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Kong Y, Fan W, Tao T, Xiao Q, Li N. et al. Principles of RNA methylation and their implications for biology and medicine. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

