Efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody, SCTA01, in high-risk outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19: A Phase II clinical trial
- PMID: 40520909
- PMCID: PMC12166818
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2025.101496
Efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody, SCTA01, in high-risk outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19: A Phase II clinical trial
Abstract
Background/objective: The neutralizing monoclonal antibody against SARS-CoV-2 is regarded as one of the most effective therapies for COVID-19.: This study was a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled Phase II trial conducted to evaluate the efficacy of neutralizing monoclonal antibody (SCTA01) in high-risk outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19.
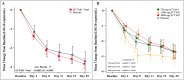
Methods: The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who experienced COVID-19-related hospitalization (defined as at least 24 h of acute care) or death (all causes) by Day 29.
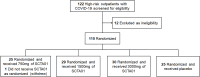
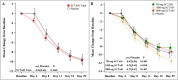
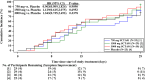
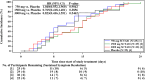
Results: 109 patients were randomly assigned to and received SCTA01 750 mg (n = 25), 1500 mg (n = 29), 3000 mg (n = 30), or placebo (n = 25). Only two experienced COVID-19-related hospitalization by Day 29, one from the 750 mg group and the other from the 3000 mg group. Statistical analysis revealed no significant differences in viral load reduction (p = 0.20) or symptom score reduction (p = 0.37) between the SCTA01 total and placebo groups. Additionally, the incidence of adverse events was comparable between the SCTA01 group (23.8 %) and the placebo group (24.0 %). Notably, no treatment-related serious adverse events (SAEs) were reported.
Conclusions: There was no significant difference in clinical outcome between SCTA01 and placebo in the treatment of high-risk outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19, and it was well tolerated.
Clinical trial: The trial was registered at ClinicalTrial.gov (NCT04709328).
Keywords: COVID-19; Neutralizing antibody; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Sinocelltech Ltd. sponsored this work. Lixin Yan, Dongfang Liu, and Liangzhi Xie are employees of Sinocelltech Co., Ltd. and have stock ownership and/or potential stock option interests in the company. All authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO COVID-19 dashboard. https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths?n=c.
-
- People with Certain Medical Conditions and COVID-19 Risk Factors. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/risk-factors/index.html.
-
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Lancet. Lancet (London, England)) 2020;395(10223):497–506. - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous