KLK8/HGF/Met signaling pathway mediates diabetes-associated hippocampal neuroinflammation in male mice
- PMID: 40521191
- PMCID: PMC12159841
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.109513
KLK8/HGF/Met signaling pathway mediates diabetes-associated hippocampal neuroinflammation in male mice
Abstract
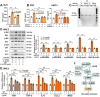
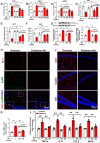
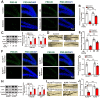
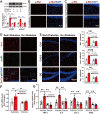
Rationale: Neuroinflammation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of diabetes-associated depression. Tissue kallikrein-related peptidase 8 (KLK8), a secreted serine protease, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of depression- and anxiety-related behaviors across various etiologies, however the underlying mechanisms remain largely unexplored. This study elucidates a novel mechanism by which KLK8 upregulation contributes to diabetes-induced microglial activation and neuroinflammation in the hippocampus through modulating the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/Met signaling pathway. Methods and Results: Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice exhibited increased KLK8 expression in the hippocampus, an effect that was mitigated in KLK8-deficient or aerobic running-exercised mice. KLK8 deficiency significantly reduced depression-like behaviors, microglial activation, and neuroinflammation in diabetic mice. In BV2 mouse microglial cells, adenovirus-mediated overexpression of KLK8 (Ad-KLK8) was sufficient to induce microglial activation. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) coupled with mass spectrometry revealed that CD44 might interact with KLK8. KLK8 overexpression decreased CD44 levels in microglial cells. However, the CD44 activator Angstrom6 further exacerbated KLK8-induced microglial activation. Conversely, transcriptional profiling of KLK8-overexpressing microglial cells and subsequent validation demonstrated that the Met/Src/Btk/NF-κB signaling pathway played a central role in mediating the stimulatory effects of KLK8 on microglial activation in both Ad-KLK8-treated BV2 cells and human microglial cell line HMC3 cells stably transfected with KLK8 lentivirus (Lv-KLK8). The Met receptor is activated upon binding to its ligand HGF, which exists as an inactive precursor (pro-HGF). Our findings showed that KLK8 cleaved pro-HGF, promoting HGF release and subsequently activating the Met/Src/Btk/NF-κB signaling pathway in microglial cells. High glucose conditions increased KLK8 expression and enhanced HGF release, thereby stimulating the Met/Src/Btk/NF-κB signaling pathway and microglial activation in a KLK8-dependent manner. Systemic administration of a Met inhibitor inactivated the Met/Src/Btk/NF-κB pathway, reducing depression-like behaviors, microglial activation, and neuroinflammation in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Both Met inhibitor and KLK8 deficiency enhanced hippocampal neuroplasticity in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Finally, we demonstrated that running exercise reversed KLK8 upregulation and inactivated Met/Src/Btk/NF-κB signaling pathways, thereby attenuating neuroinflammation, improving neuroplasticity, and alleviating depression-like behaviors in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Conclusions: This study provides evidence that the KLK8/HGF/Met signaling pathway mediates diabetes-associated hippocampal neuroinflammation and depression-like behaviors, highlighting the therapeutic potential of targeting this pathway in diabetes-associated depression.
Keywords: aerobic exercise; depression; diabetes; hepatocyte growth factor; microglia activation; neuroinflammation; tissue kallikrein-related peptidase 8.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates diabetes-induced depression-like behavior via triggering neuroinflammation.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2023 Aug 30;126:110796. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2023.110796. Epub 2023 May 19. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37209992
-
A novel role of kallikrein-related peptidase 8 in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiac fibrosis.Theranostics. 2021 Feb 20;11(9):4207-4231. doi: 10.7150/thno.48530. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33754057 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of KLK8 contributes to CUMS-induced hippocampal neuronal apoptosis by cleaving NCAM1.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Apr 19;14(4):278. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05800-5. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37076499 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling enhances pancreatic beta-cell death and accelerates the onset of diabetes.Diabetes. 2011 Feb;60(2):525-36. doi: 10.2337/db09-1305. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 20980460 Free PMC article.
-
Running exercise alleviates hippocampal neuroinflammation and shifts the balance of microglial M1/M2 polarization through adiponectin/AdipoR1 pathway activation in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable stress.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jul;29(7):2031-2042. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02464-1. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38361125
References
-
- Cooper ZW, O'Shields J, Ali MK, Chwastiak L, Johnson LCM. Effects of Integrated Care Approaches to Address Co-occurring Depression and Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2024;47:2291–2304. - PubMed
-
- Su W-J, Li J-M, Zhang T, Cao Z-Y, Hu T, Zhong S-Y. et al. Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates diabetes-induced depression-like behavior via triggering neuroinflammation. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2023;126:110796. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Xie Y, Lin J, Li M, Gu Z, Xin T. et al. Microglia Sing the Prelude of Neuroinflammation-Associated Depression. Mol Neurobiol. 2025;62(4):5311–5332. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04575-w. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

