GPA33-pretargeted radioimmunotherapy with mono- and bivalent DOTA-based Lu-177-labeled radiohaptens in a mouse orthotopic liver xenograft model of metastatic human colorectal cancer
- PMID: 40521192
- PMCID: PMC12159840
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.107209
GPA33-pretargeted radioimmunotherapy with mono- and bivalent DOTA-based Lu-177-labeled radiohaptens in a mouse orthotopic liver xenograft model of metastatic human colorectal cancer
Abstract
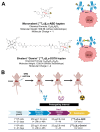
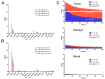
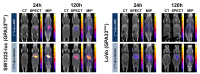
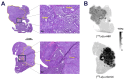
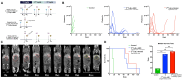
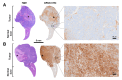
Rationale: Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy (PRIT), which combines systemic antibody-based targeting with ionizing radiation, is promising for treating liver metastases in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). Previously, we established a three-step DOTA-PRIT regimen to deliver DOTA radiometal payloads to CRC using an anti-tumor/anti-DOTA bispecific antibody (BsAb) targeting cell surface glycoprotein A33 (GPA33), a tumor antigen target expressed on over 95% of primary and metastatic CRC; a clearing agent; and a monovalent 177Lu radiohapten called [177Lu]Lu-ABD. More recently, we developed a bivalent 177Lu radiohapten called [177Lu]Lu-Gemini to enhance tumor uptake and radiohapten retention. Here, we aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of bivalent vs. monovalent three-step DOTA-PRIT regimens in orthotopic CRC liver metastasis models, to mimic a clinical path forward. Methods: We established two orthotopic CRC liver metastasis models by inoculating either SW1222-luc (GPA33high) or LoVo (GPA33low) human CRC cells in athymic nude mice under ultrasonographic guidance. Tumor targeting efficacy and dosimetry of the radiohaptens were compared using ex vivo biodistribution studies, SPECT/CT, and quantitative autoradiography. We also performed a DOTA-PRIT experiment to compare the efficacy and safety profiles of bivalent (single-cycle [177Lu]Lu-Gemini, 48 h pretargeting interval) vs. monovalent (multicycle [177Lu]Lu-ABD, 24 h pretargeting interval) three-step DOTA-PRIT regimens, each designed to deliver comparable total radiation doses to tumors (around 50 Gy). Results: Both radiohaptens demonstrated efficient SW1222-luc tumor targeting, with [177Lu]Lu-Gemini showing superior targeting and tumor activity retention compared with [177Lu]Lu-ABD. In LoVo tumors, [177Lu]Lu-Gemini showed superior targeting, while [177Lu]Lu-ABD showed negligible targeting. Dosimetry estimates revealed higher SW1222-luc tumor mean absorbed doses for [177Lu]Lu-Gemini (119.88 cGy/MBq, 48 h pretargeting interval) compared with [177Lu]Lu-ABD (32.88 cGy/MBq, 24 h pretargeting interval), with more favorable blood and kidney therapeutic indices (50 and 9 for [177Lu]Lu-Gemini, and 15 and 5 for [177Lu]Lu-ABD, respectively). In the DOTA-PRIT experiment, both monovalent (injected activity: 3 × 44.4 MBq, 133.2 MBq total) and bivalent (injected activity: 44.4 MBq total) radiohapten regimens increased the median survival of treated mice compared with controls: 71 days for [177Lu]Lu-ABD-treated mice, 81 days for [177Lu]Lu-Gemini-treated mice, and 18 days for controls, without a statistical difference between treatment groups. Treatments were well tolerated, without significant weight loss or hematologic changes. Radiation-induced injuries were not identified histologically in the kidneys or bone marrow of mice submitted for necropsy. Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the exceptional benefit of a multivalent radiohapten strategy when treating an advanced model of CRC liver metastasis. Three-step GPA33 DOTA-PRIT with 177Lu-Gemini demonstrated that multivalency 1) improves PRIT therapeutic indices for blood and kidney and 2) has the potential to greatly reduce the administered activity without compromising the efficiency of the PRIT platform in clinically relevant models of target-rich and target-poor metastatic CRC.
Keywords: Lu-177; colorectal cancer hepatic metastasis; multivalent radiohapten; pretargeted radioimmunotherapy; theranostics.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Both MSK and N.K.C. have financial interest in Y-mAbs Therapeutics, Inc., Abpro-Labs, and Lallemand-Biotec Pharmacon. N.K.C. reports receiving commercial research grants from Y-mAbs Therapeutics, Inc. and Abpro-Labs. N.K.C. was named as inventor on multiple patents filed by MSK, including those licensed to Y-mAbs Therapeutics, Inc., Lallemand-Biotec Pharmacon, and Abpro-Labs. N.K.C. is a scientific advisory board member for Eureka Therapeutics. N.K.C., S.M.L., S.M.C., D.R.V., O.O., E.K.F., G.Y., and H.X. were named as inventors on some or all the following patent applications related to GPA33: SK2014-074, SK2015-091, SK2017-079, SK2018-045, SK2014-116, SK2016-052, and SK2018-068 filed by MSK. S.M.L reports receiving commercial research grants from Genentech, Inc., WILEX AG, Telix Pharmaceuticals Limited, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; holding ownership interest/equity in Elucida Oncology, Inc. and Y-mAbs Therapeutics, Inc.; and holding stock in ImaginAb, Inc. S.M.L is the inventor and owner of issued patents both currently unlicensed and licensed by MSK to Samus Therapeutics, Inc., Elucida Oncology, Inc., and Y-mAbs Therapeutics, Inc.. S.M.L serves or has served as a consultant to Cynvec LLC, Eli Lilly & Co., Prescient Therapeutics Limited, Advanced Innovative Partners, LLC, Gerson Lehrman Group, Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. G.Y. and O.O. are listed as inventors and receive royalties from patents that were filed by MSK. O.O. is an unpaid member of the scientific advisory board of Angiogenex and owns shares in Angiogenex. D.R.V. is an inventor on intellectual property licensed to ORIC Pharmaceuticals. A.C. reports receiving research funding from GSK, Seagen, and Inspirna, and is a member of the advisory board of Bayer, GSK, Merck, Janssen, G1 Therapeutics, and Seagen. All other authors have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Theranostic GPA33-Pretargeted Radioimmunotherapy of Human Colorectal Carcinoma with a Bivalent 177Lu-Labeled Radiohapten.J Nucl Med. 2024 Oct 1;65(10):1611-1618. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.267685. J Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 39168519 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of targeting two antigens (GPA33 versus HER2) for 225Ac-pretargeted alpha-radioimmunotherapy of colorectal cancer.Theranostics. 2025 Jun 20;15(15):7489-7500. doi: 10.7150/thno.116062. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40756357 Free PMC article.
-
Curative Multicycle Radioimmunotherapy Monitored by Quantitative SPECT/CT-Based Theranostics, Using Bispecific Antibody Pretargeting Strategy in Colorectal Cancer.J Nucl Med. 2017 Nov;58(11):1735-1742. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.193250. Epub 2017 Jul 13. J Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 28705917 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

