Development and validation of a novel Simoa assay for NPTX2 in Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome
- PMID: 40522075
- PMCID: PMC12168238
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70241
Development and validation of a novel Simoa assay for NPTX2 in Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: Synaptic dysfunction and loss are pathological hallmarks of neurodegenerative diseases. Neuronal pentraxin 2 (NPTX2), a presynaptic protein involved in synaptic plasticity, has been linked to cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative disorders.
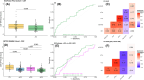
Methods: We developed and validated a novel single molecule array (Simoa) for NPTX2 in cerebrospinal fluid, which was evaluated in two independent cohorts.
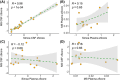
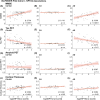
Results: CSF NPTX2 concentration was lower (fold change [FC] 0.82, p < 0.01) in AD patients and Down syndrome individuals (FC 0.56, p < 0.001), compared with cognitively unimpaired patients (CU). It was also associated with Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score (β = 2.51, p < 0.001), tau-PET (β = -0.21, p < 0.01), and cortical thickness (β = 0.08, p < 0.001).
Discussion: We describe the first assay for NPTX2 on the Simoa platform, where we continue to highlight the valuable addition of NPTX2 to routine diagnostics of suspected cognitive impairment in patients as it associates better with cognition than other, more established AD biomarkers.
Highlights: Novel method validated for measuring CSF NPTX2 on semi-automated Simoa platform. Method validated for use in CSF, where it shows a significant decrease in both AD and DS patients. Associated with cognition, neurofibrillary tangles, and cortical thickness in AD patients. Associations with cognition are shown to be stronger than those of pTau and NFL.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Simoa; biomarker; cerebrospinal fluid; down syndrome; neuronal pentraxin 2; synaptic biomarker.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, LabCorp, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures sponsored by Alzecure, BioArctic, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche, and WebMD, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). K.B. has served as a consultant and on advisory boards for Abbvie, AC Immune, ALZPath, AriBio, BioArctic, Biogen, Eisai, Lilly, Moleac Pte. Ltd., Neurimmune, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, Sanofi and Siemens Healthineers; has served at data monitoring committees for Julius Clinical and Novartis; has given lectures, produced educational materials and participated in educational programs for AC Immune, Biogen, Celdara Medical, Eisai and Roche Diagnostics; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this paper. D.A. participated in advisory boards from Fujirebio‐Europe, Roche Diagnostics, Grifols S.A., and Lilly, and received speaker honoraria from Fujirebio‐Europe, Roche Diagnostics, Nutricia, Krka Farmacéutica S.L., Zambon S.A.U., Neuraxpharm and Esteve Pharmaceuticals S.A. D.A. declares a filed patent application (WO2019175379 A1 Markers of synaptopathy in neurodegenerative disease). G.D. is the founder of LiBiCo LLC, which has no influence or contribution to the work presented in this manuscript. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures


References
-
- Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 1991;30(4):572‐580. - PubMed
-
- Halbgebauer S, Oeckl P, Steinacker P, et al. Beta‐synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid as an early diagnostic marker of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021;92(4):349‐356. - PubMed
-
- Sjögren M, Davidsson P, Gottfries J, et al. The cerebrospinal fluid levels of tau, growth‐associated protein‐43 and soluble amyloid precursor protein correlate in Alzheimer's disease, reflecting a common pathophysiological process. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2001;12(4):257‐264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

