Stumpy forms are the predominant transmissible forms of Trypanosoma brucei
- PMID: 40522086
- PMCID: PMC12169845
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.91602
Stumpy forms are the predominant transmissible forms of Trypanosoma brucei
Abstract
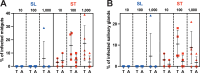
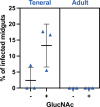
Schuster et al. demonstrated that bloodstream slender forms of African trypanosomes are readily transmissible to young tsetse flies where they can complete their complex life cycle (Schuster et al., 2021). In their experimental conditions, a single slender parasite was sufficient for productive infection. Here, we compared the infectivity of slender and stumpy bloodstream forms in adult flies with a mature immune system, and without using any chemical compounds that would alter the insect immune response and/or promote the infection. After ingestion of slender forms, infected flies were observed only in 1 out of 24 batches of non-immunocompetent teneral flies and with a high number of parasites. In contrast, infected flies were detected in 75% (18/24) of the batches infected with stumpy parasites, and as few as 10 stumpy parasites produced mature infections in immune adult flies. We discuss that, although Schuster et al. have demonstrated the intrinsic capacity of slender form trypanosomes to infect young and naive tsetse flies, highlighting the remarkable plasticity and adaptability of these protists, this phenomenon is unlikely to significantly contribute to the epidemiology of African trypanosomiases. According to both experimental and field observations, stumpy forms appear to be the most adapted forms for African trypanosome transmission from the mammalian host to the tsetse fly vector in natural conditions.
Keywords: Trypanosoma brucei; infectious disease; microbiology; slender; stumpy; transmission; tsetse fly.
Plain language summary
Human African Trypanosomiasis – also known as sleeping sickness – is a deadly disease caused by the single-celled parasite Trypanosoma brucei. The parasite has a complex life cycle that involves both humans and tsetse flies. When a tsetse fly bites an infected human, it can take up the parasite and pass it on to other people. Inside the human host, T. brucei exists in two forms: a rapidly dividing ‘slender’ form, and a non-proliferative ‘stumpy’ form that emerges once a high enough density of parasitic cells has been reached. For decades, scientists thought that only the stumpy form can successfully spread from humans to tsetse flies. However, a 2021 study challenged this view, suggesting that the slender form might also be transmissible. To investigate this further, Ngoune et al. examined whether, and under what conditions, the slender and stumpy forms of T. brucei could infect tsetse flies. The team grew both forms of the parasite in the laboratory and fed them to tsetse flies in an environment designed to resemble natural conditions. The midgut and salivary glands of the flies were then dissected four weeks later to assess the level of infection. Ngoune et al. found that slender forms of the parasite were only able to infect one out of 24 batches of young tsetse flies – and only when each fly ingested up to 10,000 parasites. The slender forms also failed to infect adult flies entirely, likely because they have a more robust immune system. In contrast, stumpy forms of the parasite where much more readily transmitted, successfully infecting about 75% of all the tested fly batches, even when as few as 10 parasitic cells were ingested. The study by Ngoune et al. reaffirms the longstanding view that the stumpy form of T. brucei is the primary stage at which the parasite is transmitted from humans to flies. While the slender form of T. brucei may be capable of infecting tsetse flies under certain conditions, these results suggest that it rarely makes this jump and is therefore unlikely to play a significant role in the spread of sleeping sickness.
© 2023, Tsagmo Ngoune et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JT, PS, AC, NP, BR No competing interests declared
Figures
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.08.30.555461
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91602.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91602.2
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91602.3
References
-
- Camara M, Soumah AM, Ilboudo H, Travaillé C, Clucas C, Cooper A, Kuispond Swar N-R, Camara O, Sadissou I, Calvo Alvarez E, Crouzols A, Bart J-M, Jamonneau V, Camara M, MacLeod A, Bucheton B, Rotureau B. Extravascular dermal trypanosomes in suspected and confirmed cases of gambiense human african trypanosomiasis. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2021;73:12–20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa897. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Capewell P, Cren-Travaillé C, Marchesi F, Johnston P, Clucas C, Benson RA, Gorman T-A, Calvo-Alvarez E, Crouzols A, Jouvion G, Jamonneau V, Weir W, Stevenson ML, O’Neill K, Cooper A, Swar N-RK, Bucheton B, Ngoyi DM, Garside P, Rotureau B, MacLeod A. The skin is a significant but overlooked anatomical reservoir for vector-borne African trypanosomes. eLife. 2016;5:e17716. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17716. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

