Rapid Identification and Typing of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Using MALDI-TOF MS and Machine Learning
- PMID: 40522100
- PMCID: PMC12168492
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.70184
Rapid Identification and Typing of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Using MALDI-TOF MS and Machine Learning
Abstract
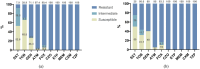
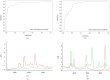
Use matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) to screen the specific mass peaks of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP), compare the differences in spectrum peaks between intestinal and bloodstream screening of CRKP, and assess the utility of MALDI-TOF MS in quickly identifying various CRKP sources. From 2014 to 2023, a total of 267 Klebsiella pneumoniae strains were collected at Quzhou People's Hospital, including 60 intestinal screening isolates from ICU patients and 207 bloodstream infection isolates. MALDI-TOF MS was used to profile peptides in CRKP and carbapenem-sensitive Klebsiella pneumoniae (CSKP), followed by analysis with flexAnalysis and ClinProTools 3.0. Statistically significant protein peaks were selected to build classification models, which were verified using non-duplicate strains. MALDI-TOF MS achieved > 99.9% accuracy in identifying Klebsiella pneumoniae. Characteristic peaks (2523.43, 3041.62, 4520.11, 10,079.18 Da) were used to develop resistance analysis models, with the optimal model (SNN) showing 90.08% sensitivity, 95.80% specificity and identification accuracies of 90% for CSKP and 89.66% for CRKP. Another model using peaks (8876, 8993, 9139 Da) differentiated CRKP origins, with the ideal model (QC) achieving 86.85% sensitivity, 88.46% specificity, and accuracies of 81.82% for bloodstream and 95.00% for intestinal CRKP.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumonia; GA; MALDI‐TOF MS; QC; SNN; bloodstream infection; carbapenemase; characteristic peak.
© 2025 The Author(s). Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ashfaq, M. Y. , Da'na D. A., and Al‐Ghouti M. A.. 2022. “Application of MALDI‐TOF MS for Identification of Environmental Bacteria: A Review.” Journal of Environmental Management 305: 114359. - PubMed
-
- Doumith, M. , Ellington M. J., Livermore D. M., and Woodford N.. 2009. “Molecular Mechanisms Disrupting Porin Expression in Ertapenem‐Resistant Klebsiella and Enterobacter spp. Clinical Isolates From the UK.” Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 63, no. 4: 659–667. - PubMed
-
- Elías‐López, C. , Muñoz‐Rosa M., Guzmán‐Puche J., Pérez‐Nadales E., Chicano‐Galvez E., and Martínez‐Martínez L.. 2024. “Porin Expression in Clinical Isolates of <styled-content style="fixed-case"> Klebsiella pneumoniae </styled-content>: A Comparison of SDS‐PAGE and MALDI‐TOF/MS and Limitations of Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis.” Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials 23, no. 1: 103. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

