HERACLIS_BLV_D: Increasing Response Rates During 2-Year Bulevirtide Real-Life Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis D
- PMID: 40522200
- PMCID: PMC12169071
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70151
HERACLIS_BLV_D: Increasing Response Rates During 2-Year Bulevirtide Real-Life Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis D
Abstract
Data availability statement: The data of this study can be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Background & aims: There is still limited real-life data for bulevirtide (BLV) therapy in chronic hepatitis D (CHD). We assessed the efficacy and safety of up to 2-year BLV therapy in CHD patients treated at Greek centres.
Methods: All patients with CHD starting BLV 2 mg before the approvals of the HERACLIS_BLV_D study were included. All patients were followed according to standard clinical practice. Serum HDV RNA was determined by a polymerase chain reaction assay at a central lab. Virological response (VR) was defined as HDV RNA undetectable or decline > 2 log10 compared to baseline. Biochemical response (BR) was defined as normal ALT.
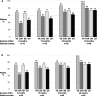
Results: Seventy-six patients were included (45 with cirrhosis). At 12 and 24 months, rates of VR were 73% and 93%, HDV DNA undetectability 57% and 80.4%, BR 71% and 74%, and combined response (VR + BR) 51% and 74%, respectively. VR response at month 24 was associated with no baseline characteristic, while 24-month HDV RNA undetectability was independently associated with lower baseline HDV RNA (p = 0.019) and platelets (p = 0.045). Both 24-month BR and combined responses were independently associated with lower baseline gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (p = 0.004) and haemoglobin levels (p = 0.006). There was no drug-related serious adverse event and no patient discontinued BLV due to an adverse event.
Conclusions: BLV monotherapy is safe and effective for the treatment of CHD patients followed at Greek tertiary liver centres offering increasing rates of VRHDV RNA undetectability and BR or combined response exceeding 90%, 80% and 70%, respectively, at 2 years of therapy.
Keywords: biochemical response; bulevirtide; hepatitis D; virological response.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. J.K. has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Abbvie, Astra‐Zeneca, Bayer, Gilead, Integris, Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis and Roche and has received research grants from Bayer, Gilead, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis and Roche. M.D. has served as lecturer for Gilead. I.E. has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Astra‐Zeneca, Gilead, Ipsen and Roche. E.S. has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Abbvie, Astra‐Zeneca, Genesis, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Ipsen, Novo Nordisk, Roche and has received research grants from Astra‐Zeneca. K.M. has served as advisor for AbbVie, Gilead, Merck Sharp & Dohme and has received grants from Gilead, Vianex and Elpen. J.V. has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Abbvie, Astra‐Zeneca, Bayer, BioArs, Galenica, Gilead, Integris Pharma, Sobi and Viatris. S.M. has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Abbvie, Astra‐Zeneca, Bioars, Gilead, Integris, Ipsen and Roche. I.G. has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Astra‐Zeneca, Gilead, Ipsen and Roche. G.D. has received research grants from Gilead and Ipsen and has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Ipsen, Gilead, Genesis, Pfizer, Sanofi and Sobi as well as principal investigator in clinical trials of Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, Intercept Pharma, CymaBay Therapeutics, Genkyotex, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Regulus Therapeutics, Sobi and Tiziana Life Sciences. G.P. has served as advisor and/or lecturer for Abbvie, Albireo, Amgen, Astra‐Zeneca, BioArs, Elpen, Genesis, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Takeda and Vir Pharmaceuticals and has received research grants from Abbvie, Gilead, Takeda and Vianex.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization , Global Hepatitis Report, 2017 (WHO, 2017).
-
- Papatheodoridi M. and Papatheodoridis G. V., “Is Hepatitis Delta Underestimated?,” Liver International 41, no. Suppl 1 (2021): 38–44. - PubMed
-
- Papatheodoridi M. and Papatheodoridis G. V., “Current Status of Hepatitis Delta,” Current Opinion in Pharmacology 58 (2021): 62–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

