Assessment of the Therapeutic Potential of Hesperidin and Quercetin Nanoparticles on Oxidative Stress, Enzyme Activities, Trophic Factors, and Monoamines in an Animal Model of Depression
- PMID: 40522360
- PMCID: PMC12170760
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-025-04447-2
Assessment of the Therapeutic Potential of Hesperidin and Quercetin Nanoparticles on Oxidative Stress, Enzyme Activities, Trophic Factors, and Monoamines in an Animal Model of Depression
Abstract
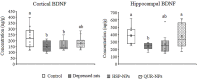
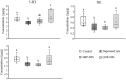
Natural remedies have emerged as promising alternative or complementary therapies for combating depression. This study aimed to investigate the effects of hesperidin (HSP-NPs) and quercetin (QUR-NPs) nanoparticles on oxidative stress markers, enzyme activities, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and monoamine levels in the cortex and hippocampus of a reserpine-induced rat model of depression. The depression model was established by administering reserpine (0.2 mg/kg) to the animals for 25 days. On the 26th, rats were administered i.p. with reserpine (0.1 mg/kg) and oral isotonic saline solution for another 21 days. Following reserpine administration, the animals exhibited a significant reduction in nitric oxide (NO), reduced glutathione (GSH), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), and dopamine (DA) levels. Additionally, a significant decrease in Na, K,ATPase activity and a significant increase in acetylcholinesterase (AchE) and monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity were observed in the cortex and hippocampus as compared to the control group of animals. Treatment with either HSP-NPs and QUR-NPs for 14 days mitigated the oxidative stress in the cortex and hippocampus. The treatments restored the changes Na, K,ATPase, and MAO, AchE activities in the two brain regions. Notably, QUR-NPs was superior in alleviating the adverse changes induced by reserpine concerning monoamines and BDNF levels. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of HSP-NPs and QUR-NPs in mitigating the underlying etiology of depressive symptoms rat model. Further investigations are warranted to exploAuthorre the potential synergistic effects of hesperidin and quercetin when used in combination at different doses and treatment durations.
Keywords: BDNF; Depression; Hesperidin; Monoamines; Oxidative stress; Quercetin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Approval: Animal’s care and experimental design were approved by the Proposal Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of Science Ain Shams University and the approval number was ASU-SCI/PHYS/2023/3/1. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the combined neuroprotective effects of resveratrol and hesperidin in a scopolamine-induced rat model of cognitive impairment.Neuroscience. 2025 Jul 23;579:54-68. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2025.05.302. Epub 2025 May 26. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 40436365
-
Scopoletin Attenuates Reserpine-Induced Pain-Depression Dyad in Mice via Modulation of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Monoaminergic Pathways.Neuromolecular Med. 2025 Jun 29;27(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s12017-025-08869-7. Neuromolecular Med. 2025. PMID: 40581693
-
Taurine protection attenuates bisphenol-A-induced behavioral, neurochemical, and histopathological alterations in male rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8525-8542. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03767-4. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39820545 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in cutaneous malignant melanoma: a proportional meta-analysis and regression.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):24-35. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae011. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38197404
References
-
- Li X, Huang W, Tan R, Xu C, Chen X, Li S, Liu Y, Qiu H, Cao H, Cheng Q (2023) The benefits of hesperidin in central nervous system disorders, based on the neuroprotective effect. Biomed Pharmacother 159:114222. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114222 - PubMed
-
- Donoso F, Egerton S, Bastiaanssen TFS, Fitzgerald P, Gite S, Fouhy F, Ross RP, Stanton C, Dinan TG, Cryan, JF O (2020) Polyphenols selectively reverse early-life stress-induced behavioural, neurochemical and microbiota changes in the rat. Psychoneuroendocrinology 116104673. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2020.104673 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

