Human placental extract rescues hippocampal damage associated with cognitive impairment in diabetic male rats through antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and neuromodulatory activities
- PMID: 40522516
- PMCID: PMC12170773
- DOI: 10.1007/s11011-025-01646-2
Human placental extract rescues hippocampal damage associated with cognitive impairment in diabetic male rats through antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and neuromodulatory activities
Abstract
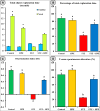
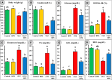
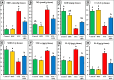
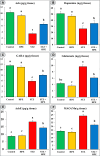
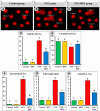
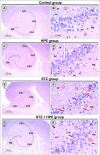
Memory and cognitive impairment have emerged as significant comorbidities associated with diabetes, yet effective treatment remains elusive. Various studies have shown that human placental extract (HPE) is rich in bioactive molecules that exhibit anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and immunomodulatory properties. However, the impact of HPE on memory and cognitive decline is not well understood. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of HPE on memory and cognitive dysfunction induced by streptozotocin (STZ) in rats, while also exploring the underlying mechanisms. To induce type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), rats were first fed a high-fat diet for two weeks, followed by a single intraperitoneal injection of STZ (40 mg/kg body weight) and subsequently treated with HPE (20 mg/kg body weight per day) for 14 days. The results of our behavioral tests demonstrated that HPE significantly enhanced learning, memory, and cognitive function in rats subjected to STZ administration. Specifically, HPE increased the discrimination index in the novel object recognition test from a negative value in STZ rats to a positive value in treated rats and improved spontaneous alternation in the T-maze from 41.25 ± 8.25% to 74.50 ± 8.50%. Additionally, HPE notably improved serum levels of insulin, glucose, the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and lipid profiles compared to untreated diabetic rats. It also modulated oxidative stress markers, antioxidants, as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines and neurochemicals levels in hippocampal tissue, underscoring its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Notably, HPE treatment improved the neurological morphology of the hippocampus and reduced DNA damage. The percentage of tailed cells dropped from 25.67 ± 0.33 in diabetic rats to 13.67 ± 0.88 with HPE treatment. In summary, HPE exhibits neuroprotective effects and could serve as a promising therapeutic strategy for addressing neurodegenerative symptoms associated with T2DM in a rat model.
Keywords: Hippocampus; Natural therapeutic products; Neuroinflammation; Neurotransmitters; Oxidative stress; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Semaglutide ameliorates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction in mouse model of type 2 diabetes.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 3;20(7):e0326897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326897. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40608828 Free PMC article.
-
Anethole Ameliorates Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits and Neuronal Damage Through Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anticholinesterase Activities in Rats.Neurochem Res. 2025 May 14;50(3):165. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04417-8. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40366448
-
Curcumin and Dementia: A Systematic Review of Its Effects on Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Outcomes in Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 21;26(14):7026. doi: 10.3390/ijms26147026. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A second act for spironolactone: cognitive benefits in renal dysfunction - a critical review.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Apr 29;40(5):194. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01623-9. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40299184 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of commercial artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) leaf powder against aflatoxin B1-induced reproductive toxicity in male rats.Mycotoxin Res. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s12550-025-00603-3. Online ahead of print. Mycotoxin Res. 2025. PMID: 40797150
References
-
- Abdelhady AA, Diab M, Nabeeh A (2021) Histological and biochemical alterations in the livers of rats treated with MSCs and placental extract against Doxorubicin as chemotherapy. Eur J Anat 25:325–338
-
- Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. In: Methods in enzymology. Elsevier, pp 121–126 - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A, Sah SP (2020) Insulin signaling pathway and related molecules: Role in neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 135:104707. 10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104707 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

