Public Water Arsenic and Birth Outcomes in the Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes Cohort
- PMID: 40522663
- PMCID: PMC12171937
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.14084
Public Water Arsenic and Birth Outcomes in the Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes Cohort
Abstract
Importance: Inorganic arsenic is associated with adverse birth outcomes, but evidence is limited for public water concentrations (modifiable by federal regulatory action) in US populations.
Objective: To evaluate the association between prenatal public water arsenic exposure below the federal regulatory standard of 10 μg/L and birth outcomes in the US.
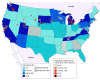
Design, setting, and participants: This cohort study analyzed observational pregnancy cohort data from the Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Cohort for birthing parent-infant dyads from 35 pregnancy cohort sites. Infants were born between 2005 and 2020. The data were analyzed between 2024 and 2025.
Exposure: Individual, time-weighted, mean prenatal public water arsenic exposures were estimated by joining Zip Code Tabulation Area-level public water arsenic concentrations with monthly residential history data during pregnancy.
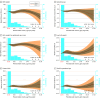
Main outcome and measure: Adjusted risk ratios (RRs) of preterm birth, low birth weight, and small for gestational age were evaluated. Adjusted RRs, mean differences in birth weight-for-gestational age z score and birth weight, and the geometric mean ratio of gestational age at birth were calculated via cubic splines, per 1 μg/L higher prenatal water arsenic, and across policy-relevant categories of exposure.
Results: The cohort comprised 13 998 birthing parents (mean [SD] age, 30.8 [5.6] years) of whom 4.5% were of American Indian, Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander; 7.2% Asian; 12.4% Black; 56.1% White; 4.2% multiple races; and 8.5% another race and 28.1% were of Hispanic/Latino and 70.4% non-Hispanic/Latino ethnicity. Prenatal public water arsenic ranged from less than 0.35 to 37.28 μg/L. In spline models, prenatal public water arsenic was associated with a higher risk of low birth weight, lower birth weight, and lower birth weight-for-gestational age z score, although effect estimates lacked precision. The RR of low birth weight per 1 μg/L higher prenatal water arsenic was higher among Black (1.02; 95% CI, 1.01-1.03), Hispanic/Latino (1.07; 95% CI 1.02-l.12), and White (1.04; 95% CI, 102-1.06) birthing parents, and the RR for preterm birth was higher among Hispanic/Latino birthing parents (1.05; 95% CI, 1.01-1.09). The mean difference of birth weight and birth weight-for-gestational age z score per 1 μg/L higher prenatal water arsenic was more pronounced among White birthing parents (-10 g [95% CI, -17 to -3 g]; -0.02 SDs [95% CI -0.03 to -0.01 SDs]). No evidence that prenatal public water arsenic mediated the association between birthing parent race and ethnicity and adverse birth outcomes was observed.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cohort study of birthing parent-infant dyads across the US, arsenic measured in public water systems was associated with birth outcomes at levels below the current US Environmental Protection Agency's maximum contaminant level. The findings suggest that further reducing the maximum contaminant level for arsenic may decrease the number of infants with low birth weight in the US.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Spaur M, Glabonjat RA, Schiling K, et al. Contribution of arsenic and uranium in private wells and community water systems with urinary biomarkers in US adults: the Strong Heart Family Study and Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and the. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2023;34(1):77-89. doi: 10.1038/s41370-023-00586-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- IRIS toxicological review of inorganic arsenic. EPA/635/R-23/166a. US Environmental Protection Agency Integrated Risk Information System . January 2025. Accessed April 1, 2025. https://iris.epa.gov/static/pdfs/0278_summary.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UG3 OD035542/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023275/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023249/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023286/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035513/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023332/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C OD023375/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035533/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023253/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES033719/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023349/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023285/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035526/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035508/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023248/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035537/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023287/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023365/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023288/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023337/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023251/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035540/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023382/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035528/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023389/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C ES026542/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035518/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023320/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023305/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035519/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035529/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES009089/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035517/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD031849/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023272/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C ES030851/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035509/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023290/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023342/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035543/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035532/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C ES026555/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035550/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023318/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023347/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD035523/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035546/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035521/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P2C HD058486/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U2C ES026561/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023279/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023348/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023268/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035536/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035527/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023282/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C ES030857/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023271/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035544/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023244/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C ES030859/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023328/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C ES026533/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023289/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023319/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023313/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023344/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035516/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 ES026539/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

