CARD8 inflammasome activation during HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission
- PMID: 40522834
- PMCID: PMC12169848
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.102676
CARD8 inflammasome activation during HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission
Abstract
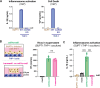
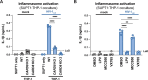
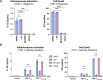
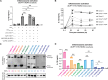
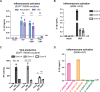
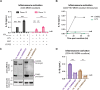
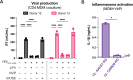
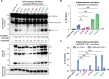
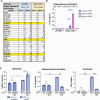
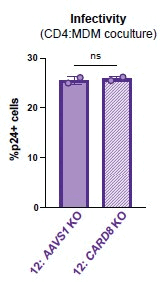
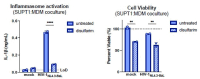
Our previous work demonstrated that CARD8 detects HIV-1 infection by sensing the enzymatic activity of the HIV protease, resulting in CARD8-dependent inflammasome activation (Kulsuptrakul et al., 2023). CARD8 harbors a motif in its N-terminus that functions as a HIV protease substrate mimic, permitting innate immune recognition of HIV-1 protease activity, which when cleaved by HIV protease triggers CARD8 inflammasome activation. Here, we sought to understand CARD8 responses in the context of HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission via a viral synapse. We observed that cell-to-cell transmission of HIV-1 between infected T cells and primary human monocyte-derived macrophages induces CARD8 inflammasome activation in a manner that is dependent on viral protease activity and largely independent of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Additionally, to further evaluate the viral determinants of CARD8 sensing, we tested a panel of HIV protease inhibitor-resistant clones to establish how variation in HIV protease affects CARD8 activation. We identified mutant HIV-1 proteases that differentially cleave and activate CARD8 compared to wildtype HIV-1, thus indicating that natural variation in HIV protease affects not only the cleavage of the viral Gag-Pol polyprotein but also likely impacts innate sensing and inflammation.
Keywords: CARD8; HIV-1; cell-to-cell; human; immunology; infectious disease; inflammasome; inflammation; microbiology; viral protease; viruses.
© 2024, Kulsuptrakul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JK, ME, PM No competing interests declared
Figures
Update of
-
CARD8 inflammasome activation during HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 15:2024.08.21.608981. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.21.608981. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 Jun 16;13:RP102676. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102676. PMID: 39229127 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bandera A, Masetti M, Fabbiani M, Biasin M, Muscatello A, Squillace N, Clerici M, Gori A, Trabattoni D. The NLRP3 inflammasome is upregulated in HIV-infected antiretroviral therapy-treated individuals with defective immune recovery. Frontiers in Immunology. 2018;9:214. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

