IFN alpha inducible protein 27 (IFI27) acts as a positive regulator of PACT-dependent PKR activation after RNA virus infections
- PMID: 40522981
- PMCID: PMC12204625
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013246
IFN alpha inducible protein 27 (IFI27) acts as a positive regulator of PACT-dependent PKR activation after RNA virus infections
Abstract
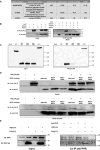
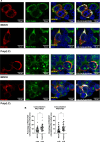
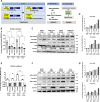
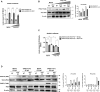
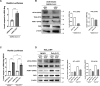
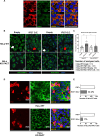
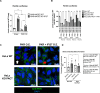
Protein kinase R (PKR) expression is induced by interferons. This protein is activated by double-stranded (ds) RNAs or RNAs containing duplex regions, produced after different stimuli, such as after viral infections, leading to the phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α), and subsequently inhibiting cellular and viral protein translation. This function may lead to different effects such as to impairing the replication of RNA viruses by inhibiting viral protein translation, and to modulating the innate immune responses after viral infections by affecting the translation of effector proteins. In this work, we identify, for the first time, an interaction of IFN alpha inducible protein 27 (IFI27) with PKR-activating protein (PACT or PRKRA) and with PKR, showing that the interaction of IFI27 with PACT is likely mediated by dsRNAs or RNAs containing duplex regions, and that the interaction of IFI27 with PKR is PACT-dependent. Interestingly, using IFI27 knocked-down, knocked-out and overexpressing tumour-derived, established cells, we show that these interactions trigger a potentiation of the activity of PKR and, therefore, a decrease in protein translation. Moreover, we find that IFI27 increases PKR function in cells infected with different RNA viruses such as Severe Acute Respiratory virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and Vesicular Stomatitis virus (VSV), and in cells transfected with the dsRNA analog poly(I:C), suggesting a broad effect of IFI27 on PKR activation. Moreover, we show that IFI27 expression increases the formation of stress granules (SGs) at the cell cytoplasm, correlating with the increased PKR activation mediated by IFI27, as it has been shown that the translational arrest induced by activated PKR leads to the formation of SGs. Mechanistically, we describe that this ability of IFI27 to activate PKR is dependent on its interaction with PACT. Further understanding of the regulation of PKR activity will allow us to develop new antiviral drugs to modulate this signalling axis, which is crucial in RNA virus infections.
Copyright: © 2025 López-García et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanism of Protein Kinase R Inhibition by Human Cytomegalovirus pTRS1.J Virol. 2017 Feb 14;91(5):e01574-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01574-16. Print 2017 Mar 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27974558 Free PMC article.
-
A MicroRNA Screen Identifies the Wnt Signaling Pathway as a Regulator of the Interferon Response during Flavivirus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02388-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28148804 Free PMC article.
-
TRBP modulates RLR signaling by inhibiting PKR-mediated antiviral stress granule formation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20678. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07121-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593223 Free PMC article.
-
NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002.NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002 Jun 10-12;19(3):1-46. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002. PMID: 14768714
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

