Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide-Based Graft-Versus-Host Disease Prophylaxis After Mismatched Unrelated Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
- PMID: 40523209
- PMCID: PMC12353616
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-25-00856
Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide-Based Graft-Versus-Host Disease Prophylaxis After Mismatched Unrelated Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
Purpose: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is a curative treatment for advanced hematologic malignancies. HSCT using human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-mismatched donors is historically associated with inferior survival. Patients from underrepresented racial and ethnic groups more frequently rely on HLA-mismatched donors. We hypothesized that post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) based graft versus host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis would improve outcomes for HSCT recipients using peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) from HLA-mismatched unrelated donors (MMUDs) by reducing the risk of GVHD.
Methods: This phase II, nonrandomized, multicenter trial assessed PBSCs in the setting of a GVHD prophylaxis regimen of cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil in two adult strata: myeloablative conditioning (MAC) and reduced-intensity or nonmyeloablative (RIC/NMA) conditioning before HSCT from a MMUD. The primary objective was to estimate 1 year overall survival (OS) for each stratum. Key secondary end points included incidences of acute and chronic GVHD.
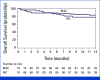
Results: A total of 145 patients enrolled, with 59% self-identifying within an underrepresented group. The 1 year OS was 83.8% (95% CI, 73.1% to 90.4%) for MAC and 78.6% (95% CI, 67% to 86.5%) for RIC/NMA. Incidences of grades III to IV acute GVHD at 6 months were 8% (95% CI, 3.2 to 15.6) for MAC and 10% (95% CI, 4.4 to 18.4) for RIC/NMA. Moderate/severe chronic GVHD at 1 year was 10.3% (95% CI, 4.4 to 18.9) for MAC and 8.6% (95% CI, 3.5 to 16.6) for RIC/NMA. 32% of patients whose donors matched at fewer than seven of eight HLA alleles had similar OS compared with those with donor matched at seven of eight alleles.
Conclusion: PTCy-based GVHD prophylaxis after MMUD HSCT with PBSC grafts results in favorable 1 year OS. Using MMUDs expands donor availability to all patients regardless of ancestry (ACCESS; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04904588).
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
This author is a member of the
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Rimando J, McCurdy SR, Luznik L: How I prevent GVHD in high-risk patients: Posttransplant cyclophosphamide and beyond. Blood 141:49-59, 2023 - PubMed
-
- Luznik L, Engstrom LW, Iannone R, et al. : Posttransplantation cyclophosphamide facilitates engraftment of major histocompatibility complex-identical allogeneic marrow in mice conditioned with low-dose total body irradiation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl 8:131-138, 2002 - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell PV, Luznik L, Jones RJ, et al. : Nonmyeloablative bone marrow transplantation from partially HLA-mismatched related donors using posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl 8:377-386, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

