Robot-assisted trigeminal nerve rhizotomy with radiofrequency ablation using Globus ExcelsiusGPS: illustrative case
- PMID: 40523350
- PMCID: PMC12171105
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE2510
Robot-assisted trigeminal nerve rhizotomy with radiofrequency ablation using Globus ExcelsiusGPS: illustrative case
Abstract
Background: Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a disorder of chronic facial pain and can be treated by radiofrequency ablation (RFA) rhizotomy of the trigeminal nerve. The use of robotic systems like the Globus ExcelsiusGPS may enhance precision and safety in intracranial procedures.
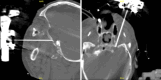
Observations: A 58-year-old male with a history of TN unresponsive to multiple treatments, including microvascular decompression (MVD) and Gamma Knife radiosurgery, underwent robot-assisted RFA rhizotomy. The Globus ExcelsiusGPS robot was used to guide a needle precisely to the gasserian ganglion through the foramen ovale. The needle's trajectory was confirmed via intraoperative CT, and RFA was performed at 70°C for 90 seconds. The procedure was well tolerated with no complications. The patient reported immediate improvement in left-sided facial pain postoperatively and was discharged the following day. At the 2-week follow-up, the patient showed resolution of preoperative symptoms. The successful implementation of robot-assisted RFA rhizotomy using the Globus ExcelsiusGPS robot for TN resulted in significant pain relief and minimal complications.
Lessons: This report demonstrates the potential of robot-assisted RFA in improving surgical precision, control, and patient outcomes in TN treatment. Further investigation into the long-term efficacy and safety of this innovative approach is warranted to fully understand its benefits and accuracy. https://thejns.org/doi/10.3171/CASE2510.
Keywords: case report; radiofrequency ablation; robotic neurosurgery; trigeminal neuralgia; trigeminal rhizotomy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Case series of CT-fusion and real-time US-guidance in percutaneous RF thermocoagulation for trigeminal rhizotomy.Pain Manag. 2025 Jun;15(6):317-323. doi: 10.1080/17581869.2025.2508683. Epub 2025 May 21. Pain Manag. 2025. PMID: 40396767
-
The influence of prior percutaneous rhizotomy on outcomes following microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia.J Neurosurg. 2023 Oct 20;140(4):1155-1159. doi: 10.3171/2023.8.JNS231345. Print 2024 Apr 1. J Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 37862713
-
Trigeminal neuralgia management in patients with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review of approaches and outcomes.J Clin Neurosci. 2025 Jun;136:111220. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2025.111220. Epub 2025 Apr 11. J Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40220576
-
Current advances in the surgical treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia.Neurosurg Rev. 2023 Feb 2;46(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s10143-023-01948-y. Neurosurg Rev. 2023. PMID: 36725770
-
Efficacy and safety of microvascular decompression with or without partial sensory rhizotomy: a comprehensive meta-analysis and systematic review in treating trigeminal neuralgia.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 May 24;47(1):229. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02463-4. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 38787487
References
-
- Zakrzewska JM Linskey ME.. Trigeminal neuralgia. BMJ. 2015;350:h1238. - PubMed
-
- De Toledo IP, Conti Réus J, Fernandes M.Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review. J Am Dent Assoc. 2016;147(7):570-576.e2. - PubMed
-
- Manzoni GC Torelli P.. Epidemiology of typical and atypical craniofacial neuralgias. Neurol Sci. 2005;26(suppl 2):s65-s67. - PubMed
-
- Obermann M Katsarava Z.. Update on trigeminal neuralgia. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009;9(3):323-329. - PubMed
-
- Maarbjerg S Di Stefano G Bendtsen L Cruccu G.. Trigeminal neuralgia—diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia. 2017;37(7):648-657. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

