Patch-type capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer for ultrasonic power and data transfer
- PMID: 40523890
- PMCID: PMC12170874
- DOI: 10.1038/s41378-025-00967-7
Patch-type capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer for ultrasonic power and data transfer
Abstract
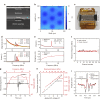
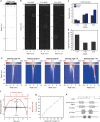
Ultrasonic power and data transfer is a promising technology for implantable medical devices because of its non-invasiveness, deep penetration depth, and potential for a high-power transmission rate with a low specific absorption rate. However, ultrasound-powered implantable devices still suffer from low power transfer efficiency due to beam misalignment and are limited to short-term use due to the bulkiness of the transmitting transducers. Here, we report the first proof of concept for adaptive positioning and targeting of ultrasound-based implantable devices through ultrasound image guidance. A lightweight patch-type ultrasonic transducer array is fabricated to enable ultrasound imaging and beam-forming during long-term operation. The uniform performance of the array is established through the silicon micromachining process. We demonstrate the complete scheme of imaging, positioning, and targeted power transfer in an ex vivo environment, achieving precise targeting of moving implanted devices through real-time ultrasound imaging. Enhanced power transfer efficiency through the use of patch-type ultrasonic transducers can enhance patient comfort and minimize invasive procedures, opening new applications for ultrasonic-powered implantable devices.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Chappel, E. In Drug Delivery Devices and Therapeutic Systems. 129–156 (Elsevier, 2021).
-
- Faro Barros, J., Sahraoui, P. F., Kalia, Y. N. & Lapteva, M. In Targeted Drug Delivery, 349–387 (Wiley, 2022).
-
- Fatima, K. et al. Long-term efficacy of spinal cord stimulation for chronic primary neuropathic pain in the contemporary era: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 68, 128–139 (2023). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
