Nanoneedles enable spatiotemporal lipidomics of living tissues
- PMID: 40523940
- PMCID: PMC12443637
- DOI: 10.1038/s41565-025-01955-8
Nanoneedles enable spatiotemporal lipidomics of living tissues
Abstract
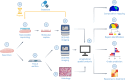
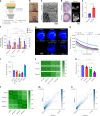
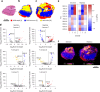
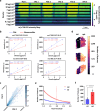
Spatial biology provides high-content diagnostic information by mapping the molecular composition of tissues. However, traditional spatial biology approaches typically require non-living samples, limiting temporal analysis. Here, to address this limitation, we present a workflow using porous silicon nanoneedles to repeatedly collect biomolecules from live brain tissues and map lipid distribution through desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging. This method preserves the integrity of the original tissue while replicating its spatial molecular profile on the nanoneedle substrate, accurately reflecting lipid distribution and tissue morphology. Machine learning analysis of 23 human glioma biopsies demonstrated that nanoneedle sampling enables the precise classification of disease states. Furthermore, a spatiotemporal analysis of mouse gliomas treated with temozolomide revealed time- and treatment-dependent variations in lipid composition. Our approach enables non-destructive spatiotemporal lipidomics, advancing molecular diagnostics for precision medicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 759577/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- BB/W006561/1/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- EP/S017607/1/RCUK | Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
- MC_PC_18052/RCUK | Medical Research Council (MRC)
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

